
What is the PAS 2080 standard?
What is PAS 2080, and how does it demonstrate a company’s dedication to carbon neutrality?
ESG / CSR
Industries



Financial tracking is fundamental to business operations, but in today's climate-conscious economy – monitoring your carbon footprint has become equally important.
Accurate carbon accounting allows your organisation to:
In this article, we'll explain what carbon accounting is, explore proven methodologies used by leading companies, and provide practical steps to implement effective carbon measurement in your organisation.
Carbon accounting, also known as greenhouse gas (GHG) accounting, is the process of measuring, tracking, and reporting carbon dioxide and other GHG emissions produced across an organisation’s operations, products, and supply chains. It forms the basis for understanding a company’s environmental impact and is critical for setting reduction targets, disclosing emissions, and meeting compliance standards.
This process provides a foundation for understanding environmental impact and helps organisations take informed actions to reduce emissions as a result of measuring the level of carbon dioxide emissions they have created. This allows them to fairly trade carbon credits between states, companies, and individuals in the carbon market.
Carbon accounting methodologies vary by industry and scope, but all aim to quantify emissions in carbon dioxide equivalent (CO₂e) — the universal metric for comparing different greenhouse gases. These calculations help organisations manage their climate strategies and engage in the carbon market, where carbon credits can be traded between companies, governments, and individuals.
In order to calculate your company’s emissions accurately, you’ll need to gather high-quality data on both direct and indirect emissions — often relying on standardised emission factors provided by bodies like the World Business Council for Sustainable Development (WBCSD).
Calculating your company's GHG emissions and overall carbon footprint often requires the collection of precise emissions data regarding both your direct and indirect emissions. This can prove challenging but luckily – there are several available types of carbon accounting software to choose from to make calculating your total greenhouse gas emissions easier, including our own platform at Greenly!


Carbon accounting has many practical uses including:
| Purpose | Description |
|---|---|
| Regulatory Compliance | Ensures adherence to local, national, and international environmental laws and carbon reporting requirements. |
| Tracking Emissions | Provides a clear picture of direct (Scope 1), indirect (Scope 2), and value chain (Scope 3) emissions. |
| Carbon Reduction Planning | Identifies high-emission areas to develop targeted reduction strategies. |
| Sustainability Reporting | Communicates an organization’s environmental performance to stakeholders through reports like CDP, GRI, or TCFD. |
| Carbon Market Participation | Facilitates the trading of carbon credits or offsets, enabling cost-effective emissions reductions. |
| Stakeholder Engagement | Demonstrates accountability and commitment to sustainability for customers, investors, and employees. |
| Cost Savings | Highlights inefficiencies in energy or resource use, potentially reducing operational costs. |
| Risk Management | Identifies potential risks from carbon-related regulatory changes or reputational damage. |
| Product Lifecycle Analysis | Assesses the carbon footprint of products, aiding eco-design and sustainable supply chain decisions. |
| Alignment with Global Goals | Supports compliance with initiatives like the Paris Agreement or science-based targets (SBTs). |
Calculating your company's GHG emissions and overall carbon footprint often requires the collection of precise emissions data regarding both your direct and indirect emissions. this can prove challenging but luckily there are several available types of carbon accounting software to choose from to make calculating your total greenhouse gas emissions easier, including our own platform at Greenly!
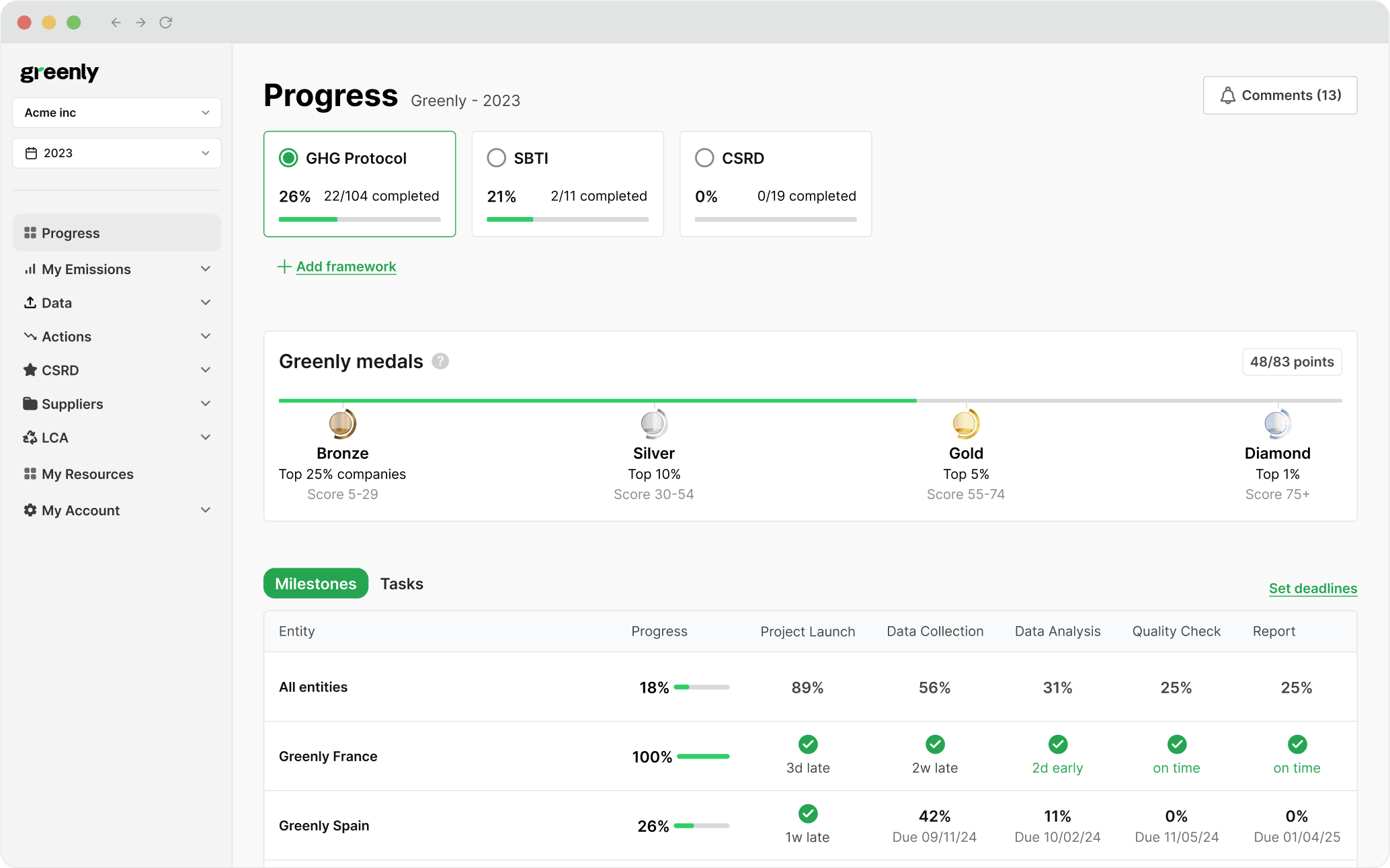
Here's the main difference between carbon accounting and a carbon assessment:
In a sense, carbon accounting is nothing more than a number – in the same vein of getting a test score back. While some people will get a bad grade on their last exam and have newfound motivation to want to do better, for others, the poor mark is nothing more than that – and it won't provoke any action or concern for potential improvement.
In short, carbon accounting provides the data and doesn't require someone to reduce their carbon emissions; carbon assessment turns that data into action. The assessment stage is where organisations identify reduction opportunities, engage with frameworks like the World Business Council’s GHG Protocol, and explore offsetting through tools such as via verified carbon credits.
At Greenly, we don’t just calculate emissions — we provide comprehensive carbon assessments to help companies reduce their footprint and embed sustainability into business strategy.
The main goal of carbon accounting is to measure, track, and report the greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions associated with an organisation's operations, products, or supply chains. This enables businesses to identify emission sources, develop reduction strategies, comply with regulations, and align with sustainability goals.
Here is an overview of key objectives of carbon accounting:
Carbon accounting relies on two main and widely used methodologies to calculate a company’s greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions: the spend-based method and the activity-based method. Both have their strengths depending on available data, goals, and timeline — and each influences how organisations measure emissions in carbon dioxide equivalent (CO₂e).
The spend-based method calculates emissions by multiplying the cost of a purchased product or service by an associated emission factor. It uses Environmentally Extended Input-Output (EEIO) models, which estimate emissions based on economic transactions across sectors.
Pros:
Cons:
When to use it:
The spend-based method is best for when time or data access is limited, and carbon calculations need to be done quickly. However, its results should be interpreted with caution due to economic variability – such as inflation or currency exchange rate fluctuations. These inaccuracies may make this method to measure carbon emissions or a company's greenhouse gas emissions less reliable basis for carbon accounting.
The second approach to carbon accounting is the activity based method.
The activity-based method provides more precise emissions data by measuring actual physical activity (e.g., liters of fuel used, kilograms of material purchased). It applies tailored emission factors to this real-world usage data, often resulting in more accurate carbon accounting.
Pros:
Cons:
When to use it:
The activity-based method is best for calculating GHG emissions when accuracy is a priority and the proper data and detailed resources are available. This makes the activity-based method particularly useful for compliance, investor reporting, and long-term sustainability planning.
Leading organisations are now often opting for a hybrid carbon accounting methodology, combining both carbon accounting methods to allow for greater accuracy and speed.
This allows companies to benefit from:
Ultimately, a hybrid approach can allow companies to build a comprehensive, credible carbon footprint — improving transparency and supporting claims in line with World Business Council protocols and other global standards.
The table below will further illustrate the key differences between the spend based and activity based methods for carbon accounting:
| Aspect | Spend-Based Method | Activity-Based Method |
|---|---|---|
| Description | Calculates emissions by multiplying the economic value of purchased products or services by relevant carbon emissions factors. | Calculates emissions based on the quantity of materials or components used, considering the actual data of physical flows. |
| Complexity | Less complex, quicker to calculate using EEIO models. | More specific and detailed, potentially more time-consuming. |
| Accuracy | Less reliable due to price fluctuations and exchange rate inconsistencies. | More accurate and precise, as it uses real data of material usage. |
| Best Use Case | Useful for quick calculations, especially when time is a constraint. | Preferred for detailed and accurate carbon accounting. |
| Hybrid Approach | Can be used in conjunction with the activity-based method for a more practical approach. | Encouraged to be used alongside the spend-based method for comprehensive accounting. |
| Example | Calculates the carbon footprint based on the price of a chair purchased. | Calculates the carbon footprint based on the quantity of materials like wood and fabric used for the chair. |
The estimated carbon emissions calculated from carbon accounting are often divided into three different categories, often referred to as, “scopes” – these scopes in carbon accounting seek to organise and simplify the process.
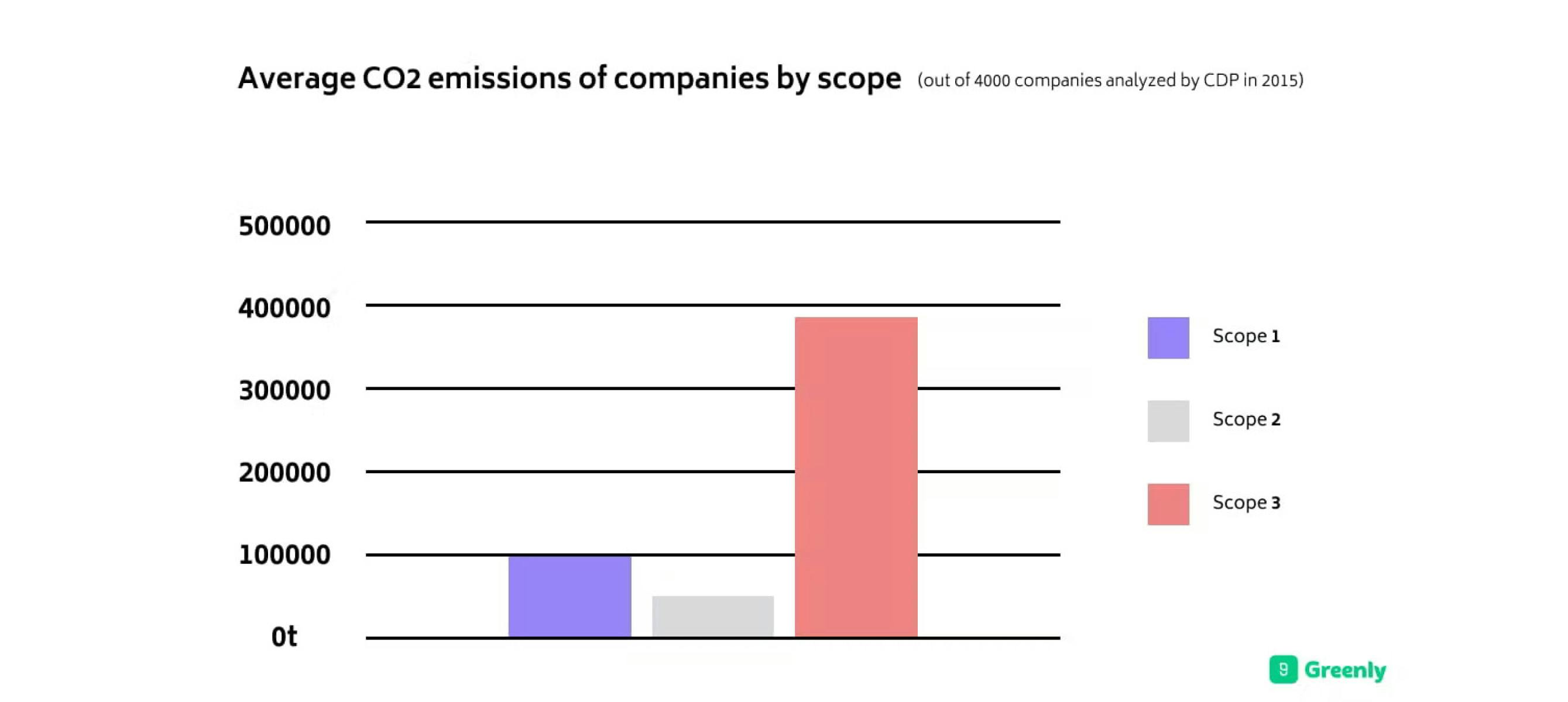
According to the Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Protocol, the three scopes are broken down whether the carbon emissions come from industrial or vehicle related activities, heating or electric cooling systems, or other various emissions that do not fall under scopes one and two.
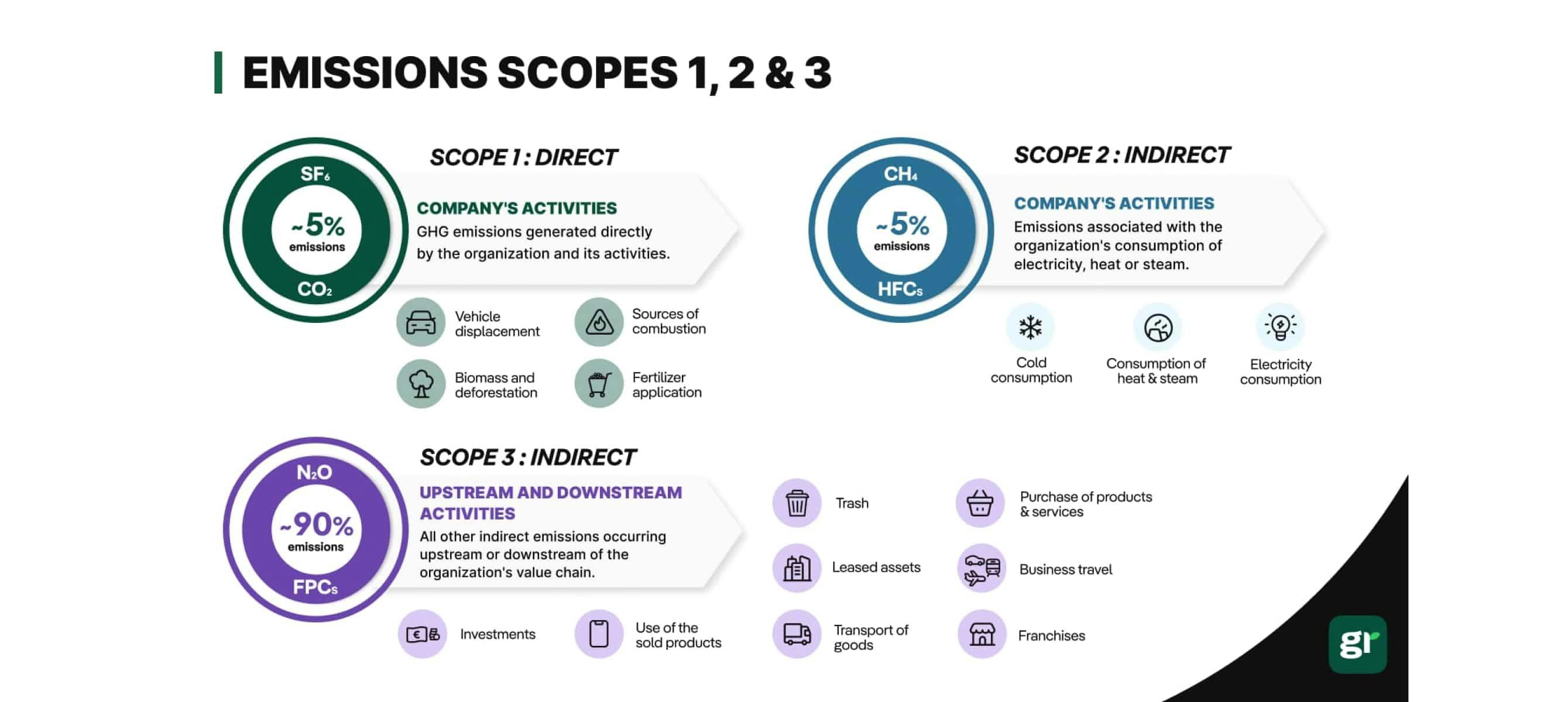
Carbon accounting relies on a clear categorisation of emissions, which are broken down into three distinct "scopes" – as defined by the GHG Protocol, the world's most widely used greenhouse gas accounting standard.
Carbon emissions are classified into the following scope categories:
These are emissions that your company directly produces through owned or controlled sources, such as from industrialisation habits or vehicles used in your company.
Here are some examples of scope 1 emissions:
Real-world example: Imagine a manufacturing company tracking emissions from its factory boilers or company-owned delivery trucks. These are direct emissions as they are produced from owned and controlled sources.
These emissions result from the generation of purchased electricity, steam, heating, and cooling that your company consumes:
Here are some examples of scope 2 emissions:
Real-world example: A big name corporation, like Google, looking to determine the carbon footprint of the electricity used to power its data centers or office buildings. These would be indirect emissions as they wouldn't be produced directly in house at Google.
Known as the largest portion of an organisation's carbon footprint, often accounting for up to 90% of a company's emissions – scope 3 emissions refer to all other miscellaneous or indirect emissions occurring in a company's value chain that don't fall under scopes one or two.
Here are some examples of scope 3 emissions:
Real-world example: A clothing retailer accounting for emissions from cotton farming, textile manufacturing, shipping, product usage, and disposal. These are miscellaneous emissions that wouldn't fall under scope 1 or scope 2 emissions data.
Remember, scope emissions are used on behalf of numerous government based and non-profit organisations to help companies break down their emissions – such as the Environmental Protection Agency and the Science Based Targets Initiative (SBTi).
As scope 3 is the most general category for carbon accounting, it is often the most difficult to precisely measure and the most challenging to reduce emissions – making it a subject of interest in carbon reporting and for businesses working towards net zero emissions.
In addition to understanding the differences between scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions – it's important to understand the disparity between key terms such as carbon neutrality and net zero.
While often used interchangeably, these terms represent different types of climate commitments –here's a breakdown of the differences between carbon neutral and net zero:
Key difference: Carbon neutrality is often a stepping stone toward net zero, as the latter requires more profound business transformation and emissions reduction – making net zero a more challenging global goal to contribute to than carbon neutrality.
The table below will demonstrate additional differences between carbon neutrality and net-zero:
| Aspect | Carbon Neutral | Net Zero |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Achieving a balance between emitting carbon and absorbing carbon from the atmosphere in carbon sinks. Typically involves offsetting emissions by investing in carbon reduction projects. | Reducing carbon emissions to as close to zero as possible and offsetting any remaining emissions. Focuses on reducing emissions through changes in processes and energy use. |
| Approach | Often relies on purchasing carbon credits to offset emissions that cannot be eliminated. | Prioritises actual reductions in emissions before considering offsets, aiming for minimal reliance on offsets. |
| Scope | Can be applied to specific activities, products, or the entire organisation. | Generally applied to the entire organisation or country, encompassing all operations and activities. |
| Long-term Goal | Maintaining a balance of emissions through continuous offsetting. | Achieving a state where no net emissions are produced, focusing on sustainable practices and renewable energy use. |
| Measurement | Often measured on an annual basis, with regular offsetting required to maintain neutrality. | Measured as a reduction trajectory over time, aiming for absolute zero emissions as much as possible. |
| Example Actions | Investing in reforestation projects, purchasing carbon offsets, improving energy efficiency. | Implementing renewable energy solutions, transforming production processes, enhancing energy efficiency, and then offsetting remaining emissions. |
| Certification | Carbon neutral certifications are available from various organisations and often involve demonstrating offset purchases. | Net zero certifications require comprehensive emission reductions and are more stringent in terms of allowable offsets. |
There are a wide variety of carbon accounting frameworks and standards to use, as organisations can rely on several established frameworks to guide their carbon accounting practices.
Here's a breakdown of the various carbon accounting frameworks and standards to help your company choose the one most suitable to your emission reduction goals:
Often known as the gold standard for carbon accounting, providing detailed methodologies for calculating emissions across all three scopes. Both their Corporate Standard and Scope 3 Standard are widely referenced in corporate sustainability reporting.
Read more about the GHG Protocol in our blog article here.
This international standard provides guidance at the organisation level for quantifying and reporting of greenhouse gas emissions and removals, which is done by providing specific verification requirements.
Read more about ISO 14064 in our blog article here.
The CDP is a global disclosure system that allows companies to measure and manage their environmental impact.
The CDP scores companies based on their climate disclosures, creating incentives for improved reporting and performance – which is becoming all the more pivotal as growing concerns around climate change continue.
Read more about the CDP in our blog article here.
While not a carbon accounting framework itself, the SBTi provides methods for setting emissions reduction targets aligned with climate science and the Paris Agreement goals.
Read more about the SBTi in our blog article here.
Developed by the Financial Stability Board, TCFD recommendations can help companies disclose climate-related financial information, including those related to carbon emissions.
Read more about the TCFD in our blog article here.
Overall, by seeking to better understand these frameworks and the fundamental concepts of emission scopes – it can help your organisations to develop a more robust climate strategy and choose carbon accounting systems that provide accurate, comprehensive data for informed decision-making and credible sustainability reporting.

There are several reasons why your company could benefit from deciding to commit to carbon accounting, such as adhering to environmental legislation, boosting brand reputation, and making process towards your company's climate goals.
Carbon accounting delivers tangible business benefits beyond environmental impact, such as :
Here's a more detailed breakdown of how carbon accounting can prove itself indispensable for decision makers and businesses:
All of the following benefits of carbon accounting ultimately attract new investors, which only continues to stimulate the economic success of the business or project.
The business case is clear – as climate risks intensify, investors are increasingly interested in companies that are willing to adjust their business model to improve overall sustainability. This reiterates how companies that use carbon accounting are likely to have a greater appeal to new investors.
Sia Partners is a consulting and accounting firm with an international presence in 18 countries that was founded in 1999. Sia Partners was tackling carbon management on its own but they were spending too much time exchanging information between their different offices. In 2020, they opted for the Greenly emissions tracking tool for greater simplicity and efficiency.
In recent years, governments and regulatory bodies around the world have implemented laws requiring companies to measure and report their carbon emissions. These regulations aim to promote transparency, accountability, and progress toward global sustainability goals.
Below is an overview of key regulations in the UK, EU, and US that mandate carbon accounting:
Many of the world's leading companies, including Microsoft, Google, and Apple, have embraced carbon accounting to measure and manage their environmental impact. Most achieve this by leveraging advanced carbon accounting software or platforms, which streamline the process and provide actionable insights for sustainability initiatives.
Here is a breakdown of how these three big-name companies make the most of carbon accounting:
Beyond environmental benefits, carbon accounting offers a range of advantages, including:
Ultimately, it plays a crucial role in combating climate change, advancing sustainable development, and ensuring businesses remain competitive and forward-thinking.
Carbon accounting and Carbon Assessment are important as they impact our environment, society, and even our global economy. Here's a breakdown of why carbon accounting and reporting are becoming more crucial by the day:
Carbon accounting is important as it encourages companies to better understand their supply chain, Scope 3 emissions, and total greenhouse gases produced to make better business decisions for the planet, people, and industry as a whole moving forward.

Remember, measuring your carbon emissions is just the beginning – as action is what drives real change.
Carbon accounting and reporting is only one step that a company can take to reduce their output of carbon emissions.
Here are 3 small and practical steps your company can take to immediately begin reducing your emissions:
Making an effort to implement smart controls for heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems across your facilities can make a big difference in your emissions.
It’s easy to accidentally leave the heat or air conditioning on in an office, car, or other rented space tied to your company when it’s unnecessary. For instance, programming automated shutdowns during unoccupied periods and establish clear protocols for holidays and weekends can help to cut back on unnecessary energy consumption and in turn – reduce overall company emissions.
This single change delivers both environmental benefits and immediate cost savings to your bottom line.
Long gone are the days where taking the metro instead of driving your car to work were the only ways to cut back on carbon emissions. Therefore, developing a comprehensive sustainable mobility program for your workforce can make a difference.
Beyond traditional public transportation subsidies, your company could consider using the following:
These initiatives directly reduce your Scope 3 emissions while improving employee satisfaction and wellness.
Conduct a space utilisation audit across your entire operation. If your company takes a moment to evaluate which rented vehicles, co-working spaces, or companies that aren’t being used to their full capacity – your company can significantly reduce both costs and carbon emissions through strategic consolidation.
This assessment can reveal opportunities to eliminate or repurpose underutilised space, allowing for optimal environmental and financial benefits.
At Greenly, we specialise in helping businesses take control of their carbon emissions through our suite of carbon management services. Whether you’re just starting your sustainability journey or looking to refine your current strategy, our platform and expertise provide the tools and insights needed to make a real impact.
Here’s how Greenly can support your business:
By working with Greenly, you’ll not only reduce your environmental impact but also boost your brand reputation, meet growing customer and investor expectations, and gain a competitive edge in an increasingly sustainability-focused world.
Ready to make sustainability a priority? Contact us today to see how Greenly can help your business take the next step toward a greener future.
EPA https://www.epa.gov/ems and https://www.epa.gov/climateleadership/scopes-1-2-and-3-emissions-inventorying-and-guidance
Harvard Business Review https://hbr.org/2022/04/we-need-better-carbon-accounting-heres-how-to-get-there
Supply Chain Solutions Center https://supplychain.edf.org/resources/carbon-accounting/
The World Business Council for Sustainable Development https://www.wbcsd.org/#
Publications Office of the European Union https://op.europa.eu/en/publication-detail/-/publication/1edb6271-5b07-40fa-ae6b-55bce1c1c220
GHG Protocol https://ghgprotocol.org/ and https://ghgprotocol.org/corporate-value-chain-scope-3-standard and https://ghgprotocol.org/corporate-standard
CDP https://www.cdp.net/en
Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures https://www.fsb-tcfd.org/
SECR UK Government https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/environmental-reporting-guidelines-including-mandatory-greenhouse-gas-emissions-reporting-guidance
Tech Informed https://techinformed.com/microsofts-carbon-negative-plans-unpacked
Sustainability at Google https://datacenters.google/operating-sustainably/
Environment Energy Leader https://environmentenergyleader.com/stories/google-has-invested-35-billion-in-renewable-energy-projects-worldwide,2747
Apple Newsroom https://www.apple.com/newsroom/2020/07/apple-commits-to-be-100-percent-carbon-neutral-for-its-supply-chain-and-products-by-2030/