
The Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM)
In this article, we break down what the EU CBAM is, how it works, and what businesses need to do to comply.
ESG / CSR
Industries



Managing an entire supply chain can prove to be difficult, especially given most companies have their suppliers located all over the world.
It takes utmost responsibility and transparency to ensure continuous safety of employees, product quality, and that social standards are still being met. Choosing a supplier is a challenging task alone, but continuing to monitor the success and effectiveness of that supplier is even more important.
👉 As our global economy and Foreign Trade Association (FTA) continues to grow, it is becoming increasingly challenging to address both business and human rights amongst global supply chains and our global market.
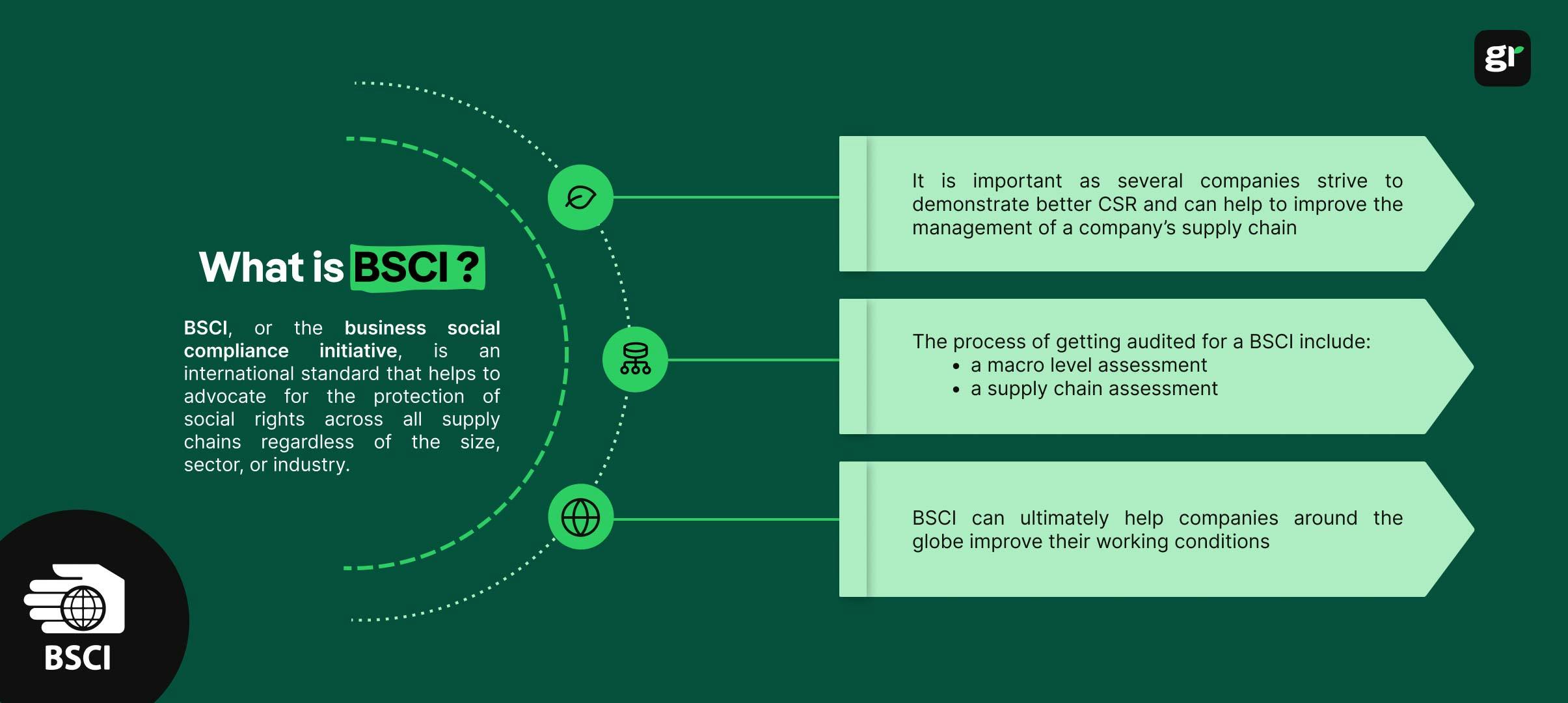
What is the BSCI, and how can it help to improve and maintain the efficiency of a businesses supply chain?
Through the implementation of a code of conduct such as BSCI, an international benchmark can be set so that all suppliers, regardless of their locale, will be supported through future effective monitoring and activity sourcing across the supply chain.
💡 The Amfori BSCI Audit, based on the International Labour Organization (ILO), refers to helping Amfori members assess both their social performance, environmental protection, and overall economic co-operation of a production site. These company policies are assessed by one of the company's own business partners within their supply chain, as this helps to focus on company policies, procedures, and common code for young workers rights moving forward.
To fully understand the importance of the BSCI code of conduct, it’s first important to understand what a supply chain is.
A supply chain is the network of the different companies or individuals who assist in the creation of a product – suppliers could include entities that provide raw materials or a factory that is essential to the manufacturing process of the product.
💡 For instance, a company creating soda cans for a carbonated drink would be considered to be a part of the supply chain – as it’s impossible to put a soda drink on the shelves to sell if it has nowhere to be bottled up.
Supply chains start with the companies that generate the raw materials necessary for the creation of the product, and they end with the final method of transportation used to deliver a product to its final destination – such as a drone or a mailman’s delivery truck.
👉 In short, without a supply chain – it is impossible to manufacture or deliver products to customers. Supply chains can manifest as real stores, vendors, and warehouses. Any place the product has been before it is sold at a store is a part of the supply chain.

Managing a supply chain is essential for all companies, and it can also help to improve efficiency in the company’s production line, reduce business costs, and ensure customer loyalty. A supply chain that is well organized can even invite new customers and investors to stimulate the business, and ultimately – help the business work towards even greater success.
💡 The BSCI code of conduct got started with supply chain efficiency in mind, as a company cannot conduct successful business regulations without applicable supply chain management.
The BSCI code of conduct started back in 2003 by the FTA, or the Foreign Trade Association – and originated as a partnership with GTZ, or the German Corporation for International Cooperation. Initially, BSCI was meant to be used to standardize working conditions for German suppliers across 11 different countries. However, the intent behind the BSCI expanded – and now, the BSCI code of conduct is headquartered in Brussels, Belgium and strives to improve working conditions in almost 2000 companies across the globe.
💡 Think of a popular company, like Apple – which initially started as a company that manufactured computers without the intent of expanding to a global extent. Now, Apple creates and sells much more than just computers – and has achieved financial success on a global scale outside of the United States, where the product was originally created.
The main goal of the BSCI code of conduct is to aid in the management of a company’s supply chain. However, the BSCI was created with several different protective social acts in mind, including the ILO, or the statements released by the International Labor Organization, the human rights principles presented by the United Nations, and the guidelines released by the OECD – or the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development.
💡 In short, the BSCI is inspired and composed of all the different ideals and values represented in these different guidelines from different international organizations.
Companies committed to following the BSCI code of conduct are expected to keep their workers up-to-date regarding their employee rights and responsibilities – as well as encourage other business partners to provide the same level of protection for their employees.
Overall, the BSCI code of conduct functions on 11 core principles such as:
Clearly, the BSCI code of conduct is multifaceted – as it can help to improve supply chain management, employee satisfaction, investor interest, overall business performance, and ultimately the environment.
How does a code of conduct as complex as BSCI get implemented into various business models?

The BSCI code of conduct gets implemented through the BSCI 2.0 – which serves as the official implementation system for companies wanting to establish the use of BSCI. Through the use of the BSCI 2.0, companies can be given advice on how to best support their suppliers and effectively incorporate the values of the BSCI code of conduct.
👉 The legal framework for the BSCI code of conduct states that all BSCI participants are subject to share their social responsibility performance with the company using them as a supplier.
In order to encourage business partner’s to implement the BSCI code of conduct into their own individual practices, BSCI participants must ask their business partners to sign a, “Terms of Implementation” document – and subsequently create an online BSCI profile for the business in question so that their progress can be monitored.
There are other methods that can be used to encourage the implementation of the BSCI code of conduct amongst a company’s business partners. A few of the ways this could be done is by reminding business partners of their clauses attached to their contracts, making a public statement on their website, or by providing a separate document stating these BSCI demands.
Many companies seek the assistance of a third party to help them implement the values depicted in the BSCI code of conduct – though this is not compulsory.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Commitment and Awareness | Companies first commit to the BSCI Code of Conduct, which requires understanding its principles and raising internal awareness. This step ensures that all stakeholders are informed about social compliance expectations. |
| 2. Risk Assessment | Conducting a risk assessment helps identify areas in the supply chain that may not comply with the BSCI standards. This involves evaluating suppliers, working conditions, and other relevant factors. |
| 3. Supplier Engagement | Companies engage with their suppliers to ensure they understand and are committed to the BSCI Code of Conduct. This may include training sessions, workshops, and providing resources to help suppliers meet compliance requirements. |
| 4. Audits and Monitoring | Regular audits and monitoring are conducted to assess whether suppliers comply with the BSCI Code of Conduct. These audits often involve third-party auditors who evaluate working conditions, wages, health and safety, and other social compliance aspects. |
| 5. Corrective Actions | If non-compliance issues are found during audits, companies must work with suppliers to develop and implement corrective action plans. This step focuses on addressing the root causes of non-compliance and improving practices over time. |
| 6. Continuous Improvement | Finally, companies and their suppliers are expected to engage in continuous improvement, regularly reviewing practices, making necessary adjustments, and ensuring long-term compliance with the BSCI standards. |

💡 If a company wants to be audited, they must seek to be audited by an official organisation that is qualified to determine whether or not the social activities being conducted by the companies are in compliance with the BSCI code of conduct.
In order to be audited for BSCI code of conduct, several resources need to be assessed and evaluated.
Here are some of the assessments that may be included in the processes of getting audited for BSCI code of conduct.
A macro-level assessment will utilise the child labor laws as depicted in the International Labor Organisation, such as ILO Convention 138 to determine if a company is acting in accordance with these laws and acts that have inspired the BSCI code of conduct in the first place.
A sectorial and supply chain assessment will specifically evaluate the effectiveness of a supply chain and how a business prioritises the management of a supply chain in their business. This can include overseeing previous and current communication with business partners and how the business handles corporate social responsibility.
👉 In addition to these assessments, businesses looking to get audited for BSCI code of conduct will also be subject to random inspections – including the random accumulation of data from other buyers, agents, or actors in conjunction with the business.
This data may be collected without warning or reference to the business in question trying to get audited for BSCI to ensure consistency of the practices depicted in the BSCI code of conduct.
Many businesses, similar to when implementing the BSCI code of conduct itself, will often seek third-party expertise to ensure the business will be audited for BSCI. Third parties may help companies to accomplish this by hiring contractors to rectify certain sectors of the business or by eschewing the manufacturing or delivery of products from places where social justice or environmentally friendly habits are not practiced.

Other important documents that BSCI auditors should keep in mind include job descriptions that would be affected by the implementation BSCI, proof of qualifications for the person in the company responsible for implementing the BSCI code of conduct, employee contracts, any written agreements between suppliers such as food and transportation, contracts with recruitment agencies, insurance documents, PPE invoices, copies of all valid business licenses, building operation certificates and proof of ability to perform business operations in said locale, documents demonstrating evidence of employee training, and all other environmental certifications – such as an ISO certification.
How difficult is it to maintain the protocols presented in the BSCI code of conduct?
The BSCI code of conduct is no easy task to implement, let alone maintain – as it requires an effort on behalf of all stakeholders, employees, business partners, and suppliers associated with a company attempting to incorporate the BSCI code of conduct or get audited for complying with BSCI standards.
However, if a business remains committed to three core principles: transparency, accessibility, and legitimacy – getting audited for BSCI and maintaining the code of conduct will not be exceptionally difficult in comparison to acquiring other environmental certifications.
In the end, complying with the BSCI code of conduct can allow a company to improve their supply chain management, improve employee safety and satisfaction, grow their business – and ultimately protect the environment.
If reading this article about BSCI code of conduct has made you interested in reducing your carbon emissions to further fight against climate change – Greenly can help you!
Greenly can help you make an environmental change for the better, starting with a carbon footprint assessment to know how much carbon emissions your company produces. Why not request a free demo with one of our experts - no obligation or commitment required.
Click here to learn more about Greenly and how we can help you reduce your carbon footprint.
