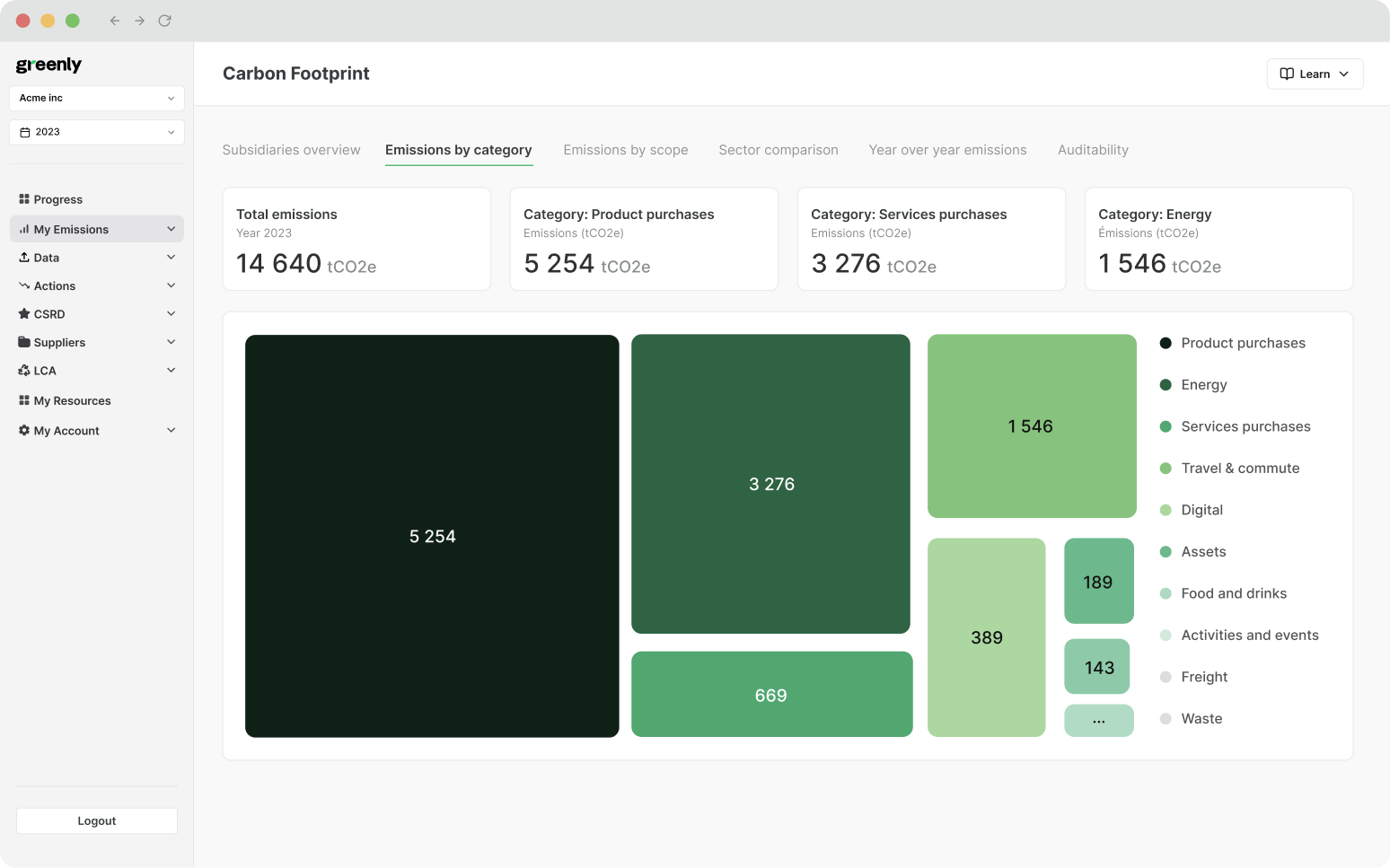
ESG / CSR
Industries
Can Tailwind Help the Aviation Industry?



- What tailwind is and how it works
- The benefits and drawbakcs of tailwind for the aviation industry
- If tailwind speeds could really help to reduce the emissions created by airline travel
After a record breaking tailwind was achieved by a China Airlines flight in January 2024, reaching a whopping 826 miles per hour – many have started to question the effects of tailwind and if it could help the aviation industry in a multitude of ways.
Accounting for 2.5% of global greenhouse gas emissions, the aviation industry often struggles to find ways to reduce its environmental impacts. Could increased tailwind speeds be the answer?
Tailwinds can help planes to travel faster, but how could that create a ripple effect to benefit the aviation industry and even the planet?
In this article, we’ll explain what tailwind is, how tailwind could benefit the aviation industry, the downsides of tailwind, and if tailwind could help in the midst of climate change.
What is Tailwind?
Tailwind refers to how fast wind is moving in the same direction as an object in motion, oftentimes – think of an airplane under this scenario.
Tailwind is a term often used in the aviation industry, but it can also be used to describe the added speed wind provides to any other moving object – such as a cyclist, runner, or a even a sailboat.
Oftentimes, tailwind is viewed as beneficial for both airline pilots and passengers – as it can often reduce air travel time and help the aircraft get to where it needs to go faster.
How Does Tailwind Work?
Wind blows from west to east, meaning that tailwind is found when the moving object is traveling east – which explains why flights from the U.S. to Europe are often shorter than traveling the other direction.
The timeline below will reveal the process of tailwind:
🔍 Choose Utility Classes
Pick Tailwind’s utility classes directly in your HTML to define layout, spacing, color, and more — no CSS file needed.
🎨 Customize via Config
Extend or override Tailwind’s design system with your own fonts, colors, breakpoints, and spacing in tailwind.config.js.
⚙️ Build with Purge
Tailwind’s JIT compiler scans your files and generates only the CSS you actually use — reducing bloat and increasing speed.
🧪 Reuse with Components
Create reusable components using class-based patterns, or pair Tailwind with tools like React, Vue, or Alpine.
🚀 Deploy & Optimize
Bundle your site with tools like Vite, Webpack, or Next.js. Tailwind is production-ready and works with modern frameworks.
Why Is It Important to Understand Tailwind Speed in Aviation?
In the midst of climate change, seeking to better understand tailwind speed is important seeing as:
- Tailwind speeds can potentially help airlines to reduce their fuel usage;
- Tailwind speeds could increase ground speed and help flying to be more time efficient and reduce airborne air-time;
- Tailwind speeds could help airlines to save money on fuel and allow available finances to implement new sustainable efforts.
The opposite of tailwind is headwind, which is when wind is coming towards the aircraft at such a high speed that it prevents the aircraft from traveling as fast as it could.
The battle cards below will breakdown the differences between tailwind and headwind:

Does Tailwind Help to Increase the Speed of an Airplane?
Tailwind absolutely helps airplanes to travel faster, as the added tailwind will help to propel the aircraft forward and increase ground speed. This is why flights are often a different length depending on which direction you go in, as tailwinds can be found when traveling east and headwinds are found when traveling west.
Therefore, a flight to New York from Paris is shorter than a flight from Paris to New York – despite the two flights needing to travel the exact same distance
Real Life Examples to Understand How Tailwind Speed Works
Another way to think of tailwinds and how it works to increase the speed of an airplane is to think of yourself on a treadmill or workout bike. If the resistance on the treadmill or other workout equipment is higher, it will be more difficult to workout at a high speed – but the lower the resistance, the faster you’ll be able to go.
The same goes for planes when dealing with the help of tailwind, lack of it due to headwind, or even crosswinds – which are winds that blow across the direction an aircraft or other vehicle is traveling.

How Could Tailwind Help Benefit the Aviation Industry?
There are several ways in which tailwind could help to benefit the aviation industry, such as helping to mitigate the need to purchase and use airplane fuel, shorter in-flight duration, and the newfound potential (as a result of additional finances from needing to use less fuel) for funding to help implement other sustainable initiatives.
Overtime, as tailwind speed increases – airlines will see themselves saving on fuel costs and also emitting less greenhouse gas emissions. These newfound additional finances could help the aviation industry to expand their sustainable efforts.
Benefits of Tailwind for the Aviation Industry
Here are some more ways that the aviation industry may benefit from increasing tailwind speeds:
- Shorter Flight Duration – As tailwind speed is expected to increase alongside warming temperatures, long-haul flights could decrease by a solid hour – which is good for both pilots to avoid fatigue and also for customers hesitant to travel for long hours.
- Add More Routes to the Flight Roster – If tailwind speeds continue to increase, some airlines may find themselves able to add more flights to their daily schedule – allowing many airlines to meet supply and demand and to provide more choices for customers. This means that tailwind speed could help to give the aviation industry an economic boost.
- Smoother In-Flight Experience – Tailwind isn’t great for take off or landing, but it can help airplanes to stabilize better while at cruising speed – offering the opportunity for a smoother in-flight experience, which can help to ease anxiety for nervous fliers.
- Reduced Emissions – Tailwind speed could help spur the need to use less fuel and cut back on costs, which in turn can allow for improved airplane models to be developed. This is especially important in the midst of the recent Boeing 747 door incident where the aircraft’s door plug fell off only a few weeks after being manufactured due to production limitations in attempts to save money.
The flip cards below (move cursor over cards to flip) will reveal additional ways that increased tailwind speeds could help the aviation industry:
The flip cards below (move cursor over cards to flip) will reveal additional ways that increased tailwind speeds could help the aviation industry:
Tailwind Speed & Climate Change
However, the most interesting potential benefit to be dissected as a result of tailwind is how increased tailwind speeds could aid in fighting against climate change. Despite the fact that increased tailwind speeds may be a result of global warming itself, greater tailwind speeds would mean that millions of flights on the daily could spend less time airborne and less time emitting fossil fuels or carbon dioxide emissions.
In fact, new research from Advancing Earth and Space Sciences reveals that as the world continues to warm up – these bursts of tailwinds, otherwise known as “jet streaks” – will continue to evolve. A study by Nature Climate Change explained that tailwinds could increase by 2% for every degree Celsius that the global surface temperature rises.
The overview cards below will reveal some of the ways that tailwind speed could help reduce the environmental impact created by the aviation industry:
The overview cards below will reveal some of the ways that tailwind speed could help reduce the environmental impact created by the aviation industry:
✈️ Faster Cruise Times
With tailwind support, planes spend less time in the air, cutting overall fuel burn and related carbon emissions per flight.
⛽ Lower Fuel Use
Boosted by tailwinds, aircraft can operate with reduced throttle and less engine thrust—directly decreasing jet fuel consumption.
🌍 Fewer Layovers
Shorter long-haul durations allow airlines to reduce connections or stopovers, which means fewer takeoffs and landings—both fuel-intensive phases.
🛠️ Less Engine Strain
Engines that run at lower output due to tailwind support experience less wear, reducing maintenance needs and resource consumption.
🌀 Optimized Flight Paths
Airlines can better design routes to take advantage of prevailing tailwinds—saving fuel and avoiding less efficient airspace corridors.
💨 Reduced Contrail Risk
Tailwind-assisted cruising can adjust altitudes to avoid contrail-forming conditions—cutting back on high-altitude warming effects.
Ultimately, this recent research indicates that the record breaking tailwind speed we recently saw with China Airlines flight 5116 may be just the beginning of drastic changes in tailwind speed.

What Are the Downsides to Tailwind in Aviation?
There are downsides to the use of tailwind, such as how tailwind is a by-product of warming temperatures and how it could prove dangerous while taking off or landing an aircraft.
Tailwind could certainly prove beneficial for the aviation industry, but these newfound wind speeds shouldn’t be the driving force behind encouraging airlines to develop a more sustainable aircraft or seek the use of bio-fuel.
One of the ways to overcome the potential setbacks of tailwind in aviation would be for airline companies to commit to employing the use of Green IT and carbon accounting services.
At Greenly, we can help companies regardless of sector or size to measure their carbon footprints with precision and develop the perfect personalized plan to reduce your business emissions and align your organization with the most recent environmental regulations and climate legislation.
Drawbacks of Tailwind for the Aviation Industry
Here are some of the reasons why tailwind may not benefit the aviation industry:
- Inconsistency – Pilots can calculate tailwind easily, but predicting it is another story – meaning that aviation pilots shouldn’t get too used to calculating tailwind into their flight patterns or models in the event there is no tailwind. Ultimately, despite the fact that tailwind could be beneficial whereas natural disasters like a wildfire or tsunami rarely are – there is no way for airlines or air pilots to foreshadow being able to reap the benefits of tailwind.
- More Difficult to Take Off & Land – Increased tailwind speeds can make it more dangerous to take off or land, as it makes ascending and descending more difficult with the added ground speed. Therefore, increased tailwind speed is only beneficial during cruising phase, so when the path diverts or when air pilots need to switch into manual mode – tailwind may no longer prove as beneficial.
- May Cause More Emissions – When tailwind is a happy accident, it certainly can help planes to reduce their fuel consumption – but this may not be the case if airlines starts to abuse increased tailwind speeds. This could happen if a, here are the irlines begin altering their travel routes to be longer in favor of tailwind speed, which in the end, ironically – could result in using more fuel.
To read more about how aviation could be decarbonized without the need for increased tailwind speeds, check out our article here!
Overall, here are the pros and cons regarding tailwind for the environmental and the aviation industry:
| Category | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Aviation Industry |
|
|
| Environment |
|
|

Is Increased Tailwind Speed Good or Bad For the Environment?
Ultimately, increased tailwind speeds could prove beneficial to the environment – but only if airlines do not take advantage of increased tailwind speeds and remain cognizant of the benefits to seeking alternative sustainable solutions.
Tailwind speeds could benefit the aviation industry by allowing the opportunity to reduce fuel consumption and create financial room to invest in other sustainable efforts – but if the aviation industry tries to manipulate the potential pros of tailwind speeds too much, it could actually result in more harm.
How Airlines Should Reduce Their Environmental Impact Long-Term
However, it’s imperative to remember that tailwind speeds are increasing as a result of a warming climate – and evidently, the potential benefits to arise from increased tail wind speeds are not worth how rising global temperatures will impact other facets of life.
For airlines to benefit from increased tailwind speeds, they shouldn’t try to maximize their current routes to match favorable weather conditions – but rather remain par the course, and benefit from reduced flight time and fuel consumption if the current tailwind speeds allow for it.
Therefore, it is crucial for the aviation industry to look for other ways to decarbonize itself without relying on faster tailwind speeds to reduce fossil fuel consumption. This can be done in many ways such as investing in further research for biofuel or offering customers the option to purchase carbon credits or carbon offsets.
The drop down sections below will reveal some of the various ways that airline companies can work to decarbonize themselves without increased tailwind speed:
The drop down sections below will reveal some of the various ways that airline companies can work to decarbonize themselves without increased tailwind speed:

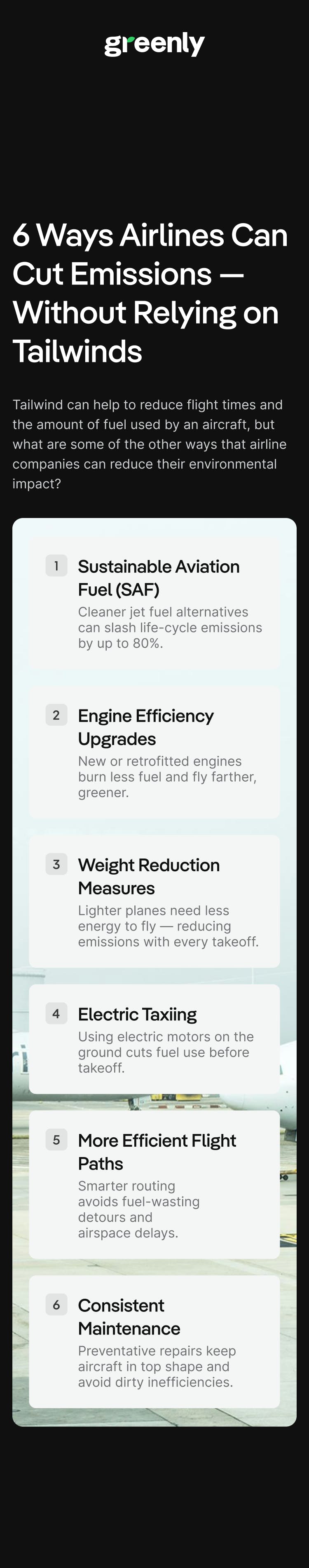
Tailwind speeds could indeed help the aviation industry to reduce their carbon footprint and overall fuel consumption – but it shouldn’t deter them from implementing other eco-friendly tactics to decarbonize this emission intensive industry.
What About Greenly?
If reading this article on tailwind and if it can help the aviation industry to be more sustainable has made you interested in reducing your carbon emissions to further fight against climate change – Greenly can help you!
At Greenly we can help you to assess your company’s carbon footprint, and then give you the tools you need to cut down on emissions. We offer a free demo for you to better understand our platform and all that it has to offer – including assistance with boosting supplier engagement, personalized assistance, and new ways to involve your employees.
Click here to learn more about Greenly and how we can help you reduce your carbon footprint.