Impacts, Risks, and Opportunities (IRO) for CSRD Reporting
In this article, we’ll break down what IROs are, how to identify and assess them, and what CSRD requires in terms of disclosure.
ESG / CSR
Industries


Sustainability reporting isn’t just something companies do to tick a box anymore. It’s become a key part of how businesses build trust, manage risk, and show what they stand for.
And it’s not just about keeping regulators happy. Research from McKinsey suggests that companies that take environmental, social, and governance (ESG) issues seriously often end up in a stronger position – more resilient, trusted, and ultimately, more valuable.
Still, for many businesses, sustainability reporting can feel abstract. What does it really involve? What are the benefits beyond compliance? And how do you get started in a way that supports your wider sustainability strategy?
There’s no one-size-fits-all format, but most reports follow recognised frameworks, like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB), or the newer European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS). These frameworks help companies stay consistent and transparent in how they report their efforts.
With so many overlapping terms, it’s easy to get confused. Here's how sustainability reporting fits into the bigger picture:
So while these terms overlap, their focus and audience differ:
| Term | Focus | Audience | Key takeaway |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Sustainability reporting
|
Broad, long-term view of environmental, social, and economic impact | Stakeholders (wide audience) | Strategic, values-driven umbrella for ESG and CSR |
|
ESG reporting
|
Financial performance and risk management | Investors, analysts | Uses similar data but focused on materiality to investors |
|
CSR reporting
|
Philanthropy, community engagement | Public, employees | Older, less data-driven, often highlights donations or volunteering |
|
Non-financial reporting
|
Any non-financial information (e.g., ethics, diversity) | Regulators, stakeholders | Broadest term, includes sustainability but not always ESG-focused |

Here are some of the key ways it creates value:
Sustainability is closely tied to long-term resilience. With climate change, resource scarcity, and social pressures creating real risks for business, sustainability reporting helps companies identify those risks early and prepare for them.
According to the Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP), 52% of companies disclosed climate-related risks with potential for significant financial or strategic impact. At the same time, 63% identified opportunities linked to climate action, highlighting how sustainability reporting can surface both challenges and areas for growth.
By tracking resource use, emissions, and waste, businesses can pinpoint inefficiencies and fix them. Sustainability reporting often uncovers areas for improvement that lead to reduced operational costs, especially when integrated with energy-saving initiatives or smarter procurement practices.
A McKinsey study found that companies combining emissions reduction with cost controls achieved up to a 40% emissions cut and a 15% boost in financial performance.
With growing pressure from regulators, customers, and investors, businesses are making more complex decisions under greater scrutiny. A robust sustainability report offers a clearer view of performance and future risk, providing the insights needed to guide your long-term management strategy, sustainability priorities, and broader business decisions.
It also helps companies prepare for tightening regulations. For example, climate-related disclosures are now mandatory in many regions, and those who already have structured reporting processes in place are better positioned to comply.
Transparency is now expected, not optional. Customers, employees, investors, and business partners increasingly want to support companies that align with their values.
Sustainability reporting gives companies a way to show, not just say, what they stand for. It provides proof of action on issues like climate change, diversity, and ethical sourcing. According to the Edelman Trust Barometer, 88% of institutional investors say companies prioritising ESG initiatives are better long-term bets.
Think of it as a blueprint; it doesn’t dictate your goals or strategies, but it gives you the tools to communicate them in a way that’s meaningful to your audience. Frameworks help ground your commitments in credible data and align your disclosures with global expectations.
Some frameworks are broad and stakeholder-focused, while others are designed specifically for investors or regulators. Depending on your objectives, you might use just one or combine several to meet different needs.
Here’s a look at the most widely used sustainability reporting frameworks and what they offer:
Focus: Broad ESG impact across environmental, social, and governance topics
Best for: Stakeholder communication, overall transparency
Key features: Covers a wide range of sustainability topics; widely adopted; aligns with SDGs
Focus: Financially material ESG issues by industry
Best for: Investor-focused reporting
Key features: Industry-specific metrics, focused on financially material sustainability performance and impact on the company
Focus: Climate-related risks and opportunities
Best for: Climate disclosure and risk management
Key features: Developed by the International Sustainability Standards Board (ISSB); focuses on governance, strategy, risk management, and metrics; adopted into IFRS
Focus: Climate, water, and forest impact disclosures
Best for: Benchmarking environmental performance
Key features: Questionnaire-based; aligned with TCFD; includes scoring system
Focus: Integrated reporting of financial and non-financial performance
Best for: Communicating long-term value creation
Key features: Emphasises connectivity between ESG and financial data
Focus: Mandatory ESG disclosures in the EU
Best for: EU-based or EU-operating companies
Key features: Requires audited, standardised sustainability disclosures aligned with ESRS
Focus: Social responsibility and ethical behaviour
Best for: Voluntary guidance for CSR integration
Key features: Covers topics like human rights, labour, and governance
Focus: Alignment with the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals
Best for: Companies committed to global responsibility
Key features: Encourages transparency across 10 principles of the UNGC
You don’t need to follow every framework, just the ones that make sense for your business. The right fit depends on your goals, stakeholders, and reporting requirements, whether driven by regulation or internal strategy.
Here are a few things to consider:


Whether sustainability reporting is mandatory depends on where your business operates, your industry, and your size.
In some regions, particularly the EU, reporting is no longer optional. Under the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), thousands of companies are now required to disclose detailed sustainability information.
Other jurisdictions are following suit – the UK has introduced mandatory climate-related financial disclosures for large companies, and the US is rolling out stricter SEC rules for listed firms.
While many companies are currently focused on meeting new regulatory requirements, sustainability reporting is moving far beyond basic compliance. Over the next few years, several trends are expected to reshape how businesses disclose and manage ESG data:
Sustainability reporting has become a core element of corporate governance in the UK, shaped by regulation, investor pressure, and evolving market expectations. Here’s what companies operating in the UK need to know:
The UK has introduced a mix of mandatory and voluntary reporting measures:
UK companies often adopt international sustainability reporting frameworks to align with global best practices and meet stakeholder demands. The most commonly adopted frameworks in the UK include:
| Framework | Focus | Best suited for | Mandatory / Voluntary |
|---|---|---|---|
|
🌍 Global Reporting Initiative (GRI)
|
Broad ESG issues across environment, social, and governance | Companies wanting comprehensive sustainability reports for stakeholders | Voluntary |
|
📑 Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD)
|
Climate-related risks and opportunities | Large UK companies, investor-focused climate reporting | Mandatory for large companies (moving to IFRS S1/S2 by 2026) |
|
📊 Carbon Disclosure Project (CDP)
|
Environmental impacts (climate, water, forests) | Companies aiming to disclose environmental data for benchmarking and investors | Voluntary |
|
📈 Sustainable Accounting Standards Board (SASB)
|
Industry-specific, financially material ESG topics | Investor-focused reporting, companies seeking detailed sector metrics | Voluntary |
|
📜 Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD)
|
Standardised ESG disclosures aligned with ESRS | UK companies operating in the EU or wanting EU-aligned reporting | Mandatory for in-scope EU companies |
Investors continue to integrate ESG factors into decisions:
Principles for Responsible Investment (PRI)
Many UK-based investors are signatories to the PRI, which promotes the integration of ESG issues into investment practice.
UK Stewardship Code
This Code sets high standards for responsible investment, requiring signatories to report on how they have applied the Code's principles, including their approach to ESG issues.
Sustainable Finance Disclosure Regulation (SFDR)
Although primarily an EU regulation, UK investors and companies with operations in the EU are influenced by SFDR, which mandates transparency in sustainability-related disclosures.
The UK market is experiencing a growing demand for sustainability from both consumers and businesses. Key trends include:

Getting started with sustainability reporting doesn’t have to be overwhelming. By breaking the process into a few clear steps – from identifying what matters most to choosing the right framework and collecting the right data – you can build a report that’s both practical and meaningful.
Here’s a simple step-by-step approach to get started:
The steps below outline how to create a sustainability report:
1. Identify what matters most 🔍
Start by figuring out which sustainability topics are most relevant to your business and stakeholders. This could include emissions, energy use, supply chain ethics, employee wellbeing, or waste. Tools like stakeholder surveys or materiality assessments can help you focus your efforts where they’ll have the most impact.
2. Choose your reporting framework 📑
Pick the framework (or combination) that best fits your goals, industry, and legal obligations. Whether it’s GRI for broad transparency, SASB for investor relevance, or CSRD for EU compliance, your framework will shape what and how you report.
3. Collect your data 📊
You’ll need both qualitative insights and hard numbers – from emissions data and diversity metrics to supply chain policies and social initiatives. Make sure your data sources are reliable, and validate your figures where possible to maintain credibility.
4. Build your report 🏗️
Organise your content around the framework’s structure. Use plain language, include data visuals where helpful, and explain the story behind your numbers. Many companies also include case studies or goals to show progress and ambition.
5. Publish and engage 📢
Once the report is ready, share it on your website, with investors, internally, and across other relevant channels. The aim isn’t just to tick a box, but to open up a conversation with the people your business impacts.
6. Track progress and keep improving 🔄
Sustainability reporting isn’t a one-off task – it’s part of an ongoing process. Keep reviewing your data, tracking against your goals, and updating your stakeholders on progress year over year.
Sustainability reporting can quickly become complex. From gathering Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions data to aligning with multiple frameworks like GRI, SASB, and CSRD, businesses often face:
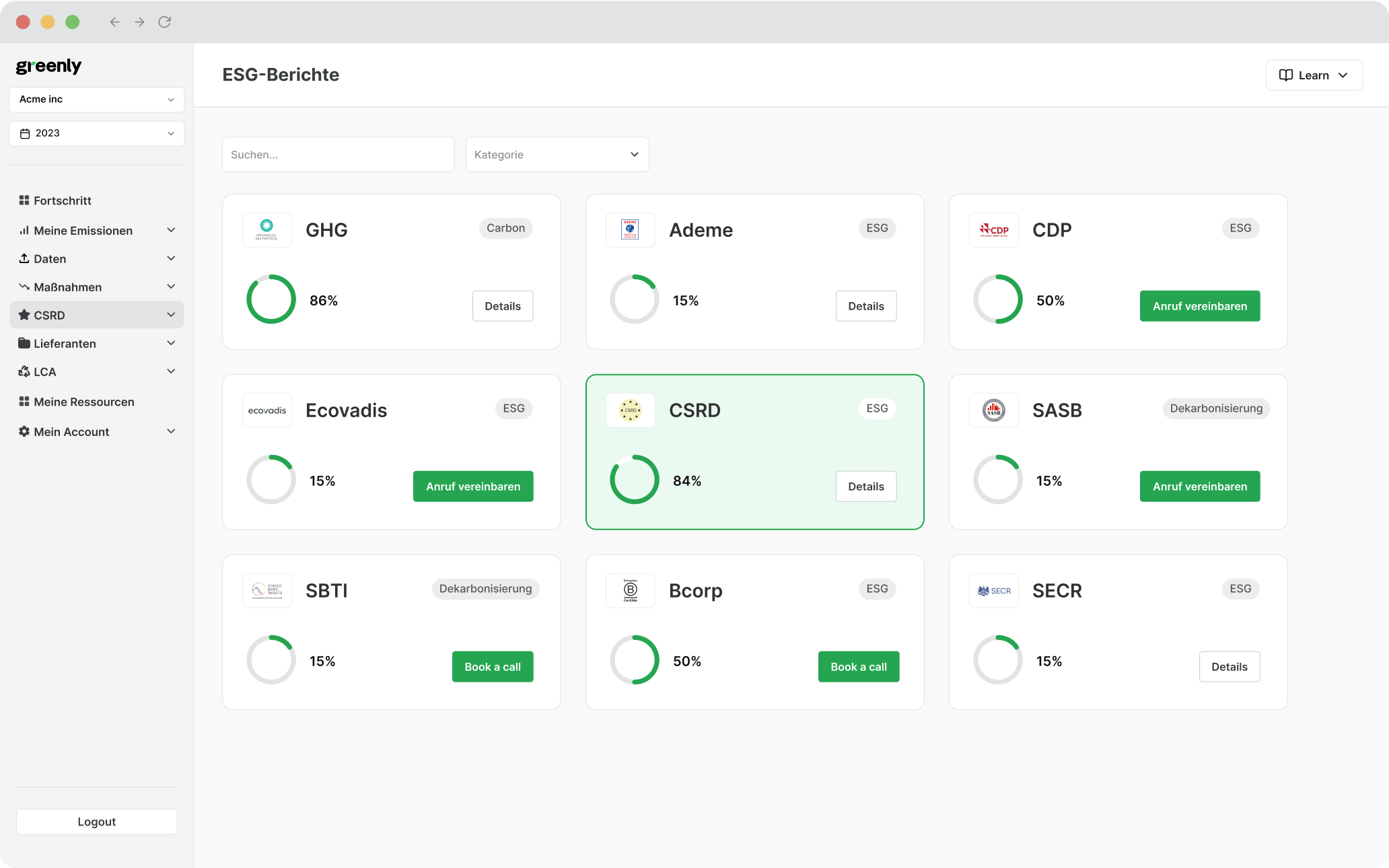
Below, we’ve compiled a comparison of the top 10 sustainability reporting tools in 2025, with Greenly ranked #1 for its comprehensive carbon management capabilities and ease of use.
| Rank | Tool / Platform | Best for | Key features | Pricing model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 |
Greenly | SMEs and large enterprises looking for all-in-one carbon management and ESG reporting | - Automated carbon footprint tracking - LCA and Scope 1, 2, 3 analysis - Reporting for CSRD, IFRS S1/S2, GRI, SASB - Supplier engagement tools |
Subscription-based; tailored to company size |
2 |
Sphera | Large enterprises with complex reporting needs | - Advanced ESG data management - Risk and compliance dashboards - Supports multiple reporting frameworks |
Enterprise licensing |
3 |
Workiva | Companies focused on financial + sustainability reporting integration | - Unified platform for SEC filings and ESG data - Cloud collaboration - SASB, TCFD alignment |
Subscription-based |
4 |
Persefoni | Organisations needing carbon accounting expertise | - AI-driven carbon data insights - Financial-grade climate disclosures - Partnership with consulting firms |
SaaS model |
5 |
Envizi (by IBM) | Enterprises aiming for deep analytics | - ESG reporting automation - Data visualisations and KPI dashboards - Supports CDP submissions |
Subscription-based |
6 |
Cority | Industries with strict compliance requirements (e.g., manufacturing) | - EHS and ESG integration - Data audit trails - Assurance-ready reports |
Tiered pricing |
7 |
FigBytes | Mid-sized businesses looking for ESG strategy alignment | - Visual ESG roadmapping - SDG reporting modules - Multi-framework compatibility |
SaaS model |
8 |
Diligent ESG | Companies prioritising governance and board-level reporting | - Governance and risk management focus - Board-ready dashboards - ESG performance tracking |
Subscription-based |
9 |
VelocityEHS | Businesses needing scalable sustainability management | - Environmental data management - KPI and target tracking - Cloud reporting tools |
SaaS model |
10 |
Measurabl | Real estate and property management firms | - Energy and sustainability metrics for buildings - GRESB and CDP reporting support - Automated data capture |
Subscription-based |
The best sustainability reporting software depends on your organisation’s size, reporting requirements, and future ESG goals. When evaluating tools, consider:
Framework coverage
Does it support the standards you need to report under, such as CSRD, GRI, or IFRS S1/S2?
Automation
Can it streamline data collection and reduce reliance on manual spreadsheets?
Scalability
Will it handle growing data volumes, multiple sites, or complex supply chains?
Assurance-ready outputs
Does it provide clear dashboards and audit-friendly reports for stakeholders?
Choosing a tool that meets these criteria ensures sustainability reporting is accurate, efficient, and a true driver of long-term business value.
A: It means collecting and disclosing data on how a company affects the environment, society, and economy – from emissions and energy use to supply chain practices and diversity initiatives – and presenting it in a structured, framework-aligned report.
A: Not everywhere. In the EU, the CSRD now makes reporting mandatory for thousands of companies. The UK has introduced climate-related financial disclosures, and the US is tightening SEC rules. Elsewhere, many companies report voluntarily to meet investor and stakeholder expectations.
A: Popular choices include GRI for overall transparency, SASB and IFRS S1/S2 for investor-focused reporting, CSRD and ESRS for EU requirements, CDP for environmental benchmarking, and ISO 26000 for CSR integration.
A: Most companies issue annual reports alongside financial statements. Organizations with ambitious climate targets or regulatory obligations may release interim updates to track progress.
Sustainability reporting is only one piece of the puzzle. To truly move from reporting to real climate impact, businesses need tools that can measure, manage, and reduce emissions across their entire value chain.
Greenly offers a comprehensive suite of sustainability solutions designed to streamline reporting and strengthen climate action:
| Greenly Solutions | What It Provides |
|---|---|
|
Carbon footprint assessments
|
Measure Scope 1, 2, and 3 emissions across operations, supply chains, and products with precision. |
|
Compliance-ready reporting
|
Produce disclosures aligned with GRI, CDP, TCFD/IFRS S2, and CSRD, ensuring alignment with evolving regulations. |
|
Life Cycle Assessments (LCA)
|
Gain a full understanding of product and service environmental impacts to guide sustainable decision-making. |
|
Decarbonisation strategies
|
Set science-based targets and build actionable, high-impact emission reduction plans with expert support. |
|
Sustainable procurement support
|
Identify greener suppliers and improve sustainability performance throughout your value chain. |
Whether you're reporting to stakeholders, preparing for regulation, or looking to build a long-term climate strategy, Greenly’s platform and team are here to help. Get in touch to see how Greenly can support your goals.