What are the 3 Pillars of Corporate Sustainability?
In this article, we'll explore what the 3 pillars of corporate responsibility are, why they're important, and how businesses can turn them into practical action.
ESG / CSR
Industries



In 2025, shifting to the use of more sustainable packing materials and attempting to go green are all ways that the average person and business take a step forward to fighting against climate change – such as by employing the use of biodegradable plastic.
Biodegradable and compostable plastic are becoming increasingly common, as several businesses decide to revamp their packaging to offer more eco-friendly products – but how beneficial is biodegradable plastic, truly?
In this article, we’ll explain what biodegradable plastic is, the pros and cons, and better alternatives to help the environment.
Biodegradable plastic refers to the ability for plastic to break down into substances, such as bacteria, fungi, and algae – in a short amount of time.
💡 The main goal of biodegradable plastic is to speed up the process of plastic breaking down, as traditional plastics can take hundreds of years to fully decompose – biodegradable plastic can be broken down into natural elements such as water, carbon dioxide, and biomass.
Biodegradable plastic decomposes as microorganisms will use the plastic as a food source, which will then break it down into simpler substances to be absorbed into the surrounding environment, such as a nearby body of water.
👉 However, it is important to note that environmental factors also play a role – as humidity, sunlight, and temperature can have an impact on how fast biodegradable plastic decomposes.
There are two main types of biodegradable plastics: plant-based biodegradable plastic and petroleum based biodegradable plastic.
👉 Biodegradable plastic is often used for packaging materials, agricultural films, and even for dissolvable stitches – demonstrating the versatility of biodegradable plastics and the opportunity it has to help reduce plastic waste across multiple industries.

While both biodegradable and compostable plastics can break down into their surrounding environment, the two types of plastic are not one and the same.
💡 Biodegradable plastic is defined by its ability to break down, but may not always prove successful – whereas compostable plastic is developed and tested to ensure it will work when it undergoes processing in a composting facility.
Overall, the main difference between biodegradable and compostable plastic is their ability to break down into the environment.
Here’s a breakdown of the differences between the these two types of plastics:
The table below will compare and contrast the differences between biodegradable and compostable plastic:
| Feature | Biodegradable Plastic | Compostable Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Breakdown Time | Varies (weeks to years) | Typically faster (weeks to months) |
| Breakdown Residue | Possible microplastics | No toxic residues, turns into compost |
| Conditions Needed | May break down in natural settings | Requires specific composting conditions |
| Certification | Not always certified | Must meet strict standards |
| Environmental Impact | Can be unclear (if not fully degraded) | More environmentally friendly |
👉 Ultimately, compostable plastics are a better choice for the circular economy as they can completely break down without leaving behind any residue – whereas biodegradable plastics may still contribute to plastic pollution as they do not undergo the same approval process as compostable plastics.

There are several benefits and drawbacks to the use of biodegradable plastic, such as how it can help to mitigate excessive plastic pollution – but it also requires specific conditions and could exacerbate the danger of misleading eco-labels.
💡Although biodegradable plastic can help to avoid the negative effects of plastic lingering in our oceans and surrounding environment, it is important to note that at the end of the day – biodegradable plastic is still a type of plastic, meaning that it isn’t the most sustainable material or resource to be using in the midst of climate change.
This was demonstrated in a study conducted by Imogen Napper, where it was found that biodegradable plastic shopping bags were still present in soil a whopping 27 months after being buried – illustrating how biodegradable plastic still remains present in our environment despite being able to break down faster than traditional plastic.
All of this being said, there are still reasons to opt for the use of biodegradable plastic while keeping the disadvantages in mind.
Here’s a breakdown of the pros and cons of biodegradable plastic:
👉 Overall, biodegradable plastic is certainly a more viable alternative to the use of traditional plastics – but it still possesses several potential setbacks, such as by potentially contributing to microplastic pollution or proving to be too expensive for some companies.
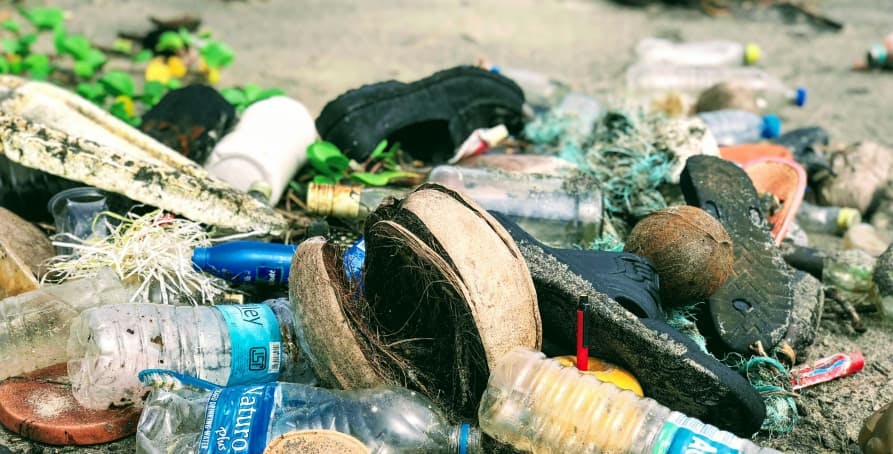

Biodegradable plastic, while a better alternative than traditional plastic, can still end up in landfills and contribute to the release of methane – ultimately still contributing to GHG emissions.
💡This means that when bioplastics end up in the landfill, of which many do, they can contribute to potent greenhouse gases in the same capacity of PET plastic.
Unfortunately, this hasn’t stopped big-name companies from insinuating that plastic pollution can be solved with biodegradable plastic – such as with Coca-Cola, from using vague terms to convince customers that their products are not contributing to further environmental harm.
Luckily, to combat the effects of plastic pollution – Coca-Cola has committed themselves to recycle one plastic bottle for every bottle it sells by 2030. While recycling can help, such as in regions of the world like Europe where 41% of plastic was recycled in 2022 – efforts to encourage consumers to recycle plastic, even biodegradable plastic, could prove pointless in countries which value consumerism like the U.S. – where only 8.4% of plastic is recycled.
Additional reasons why biodegradable plastic may not be the best solution include:
👉 As a whole, biodegradable plastic is surely better than traditional plastic as it has a better chance of being decomposed and mitigating excess GHG emissions – but there are still better alternatives than biodegradable plastic.

There are several alternatives to the use of biodegradable plastic, such as:
Overall, biodegradable plastic is a type of plastic that can be broken down into the environment faster than traditional plastic – but it still isn’t the most efficient way to support the planet or mitigate climate change.
If reading this article on biodegradable plastic has inspired you to consider your company’s own carbon footprint, Greenly can help.
At Greenly we can help you to assess your company’s carbon footprint, and then give you the tools you need to cut down on emissions. We offer a free demo for you to better understand our platform and all that it has to offer – including assistance on how to reduce emissions, optimize energy efficiency, and decarbonize your supply chain to help reduce plastic waste.
Learn more about Greenly’s carbon management platform here.