The Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM)
In this article, we break down what the EU CBAM is, how it works, and what businesses need to do to comply.
ESG / CSR
Industries



Seaweed might look like an unlikely contender for a potentially scalable solution to climate change, but this slimy-looking brown kelp is starting to attract interest across the globe. Capable of storing carbon, protecting local communities from the impacts of climate change, and even offering a potential solution to the growing plastic crisis, seaweed farming offers a range of environmental benefits.
Seaweed farming, also referred to as kelp farming, is the practice of cultivating and harvesting seaweed or algae. Traditionally, the practice was mainly found in South East Asia, in countries such as China, Indonesia, and the Philippines, however, in recent years, its popularity has grown and seaweed farming is now practised across the globe. In fact, it's the fastest-growing aquaculture sector worldwide.
👉 Global production of seaweed was 10.6 million tonnes in 2000, but has since grown to 35.1 million tonnes in 2020.
There are a variety of different methods for farming seaweed, depending on the climate and country in which it’s grown.
Seaweed has many uses, including:
Chemicals
Chemicals from seaweed feed industrial, pharma, cosmetic, and food sectors. Key derivatives include carrageenan (natural gelling agent) and agar (stabilising gel for texture and thickening).
Food
Seaweed is fibre-rich and widely used in Asian cuisine. Its extracts also act as water retainers, gelling and emulsifying agents across many products.
Fuel
Algal biofuel offers an alternative to land-intensive biofuels (e.g., corn, sugarcane) by converting seaweed biomass into liquid fuels or biogas.
Bioplastics
Polymers from seaweed (e.g., alginate) can be used to make biodegradable films, packaging, and coatings—reducing reliance on fossil-based plastics.
Fertilisers & soil
Seaweed extracts are used as bio-stimulants and fertilisers—improving soil structure, nutrient uptake, drought tolerance, and plant resilience.
Animal feed
As a feed additive, seaweed can improve animal health and, in some cases, help reduce enteric methane when used in controlled formulations.
Bioremediation & carbon
Seaweed absorbs excess nutrients and CO₂, supporting water quality and offering potential blue-carbon co-benefits when responsibly managed.

The rapid rise in seaweed production is also, in part, being fuelled by the growing realisation that seaweed has a number of environmental benefits and eco uses. It’s a ‘zero input’ crop that leaves the ocean healthier with each seaweed harvest cycle.
In this next section, we’ll explore why seaweed farming is creating so much excitement in terms of climate change mitigation and adaptation.
Seaweed production functions as a form of carbon sequestration. In other words, this means that seaweed is able to capture carbon dioxide from the environment and store it - something that both reduces the amount of carbon in our atmosphere and diminishes ocean acidification.
Seaweed captures the carbon dioxide through photosynthesis, a process that it uses to create energy and to grow. This carbon is then stored as organic matter. Part of this organic matter eventually becomes waste or debris and is carried to the deeper ocean - something that is termed blue carbon.
Due to the low concentration of oxygen underwater (particularly at deeper depths) the plant material can stay buried for decades or longer before breaking down and releasing carbon back into the environment.
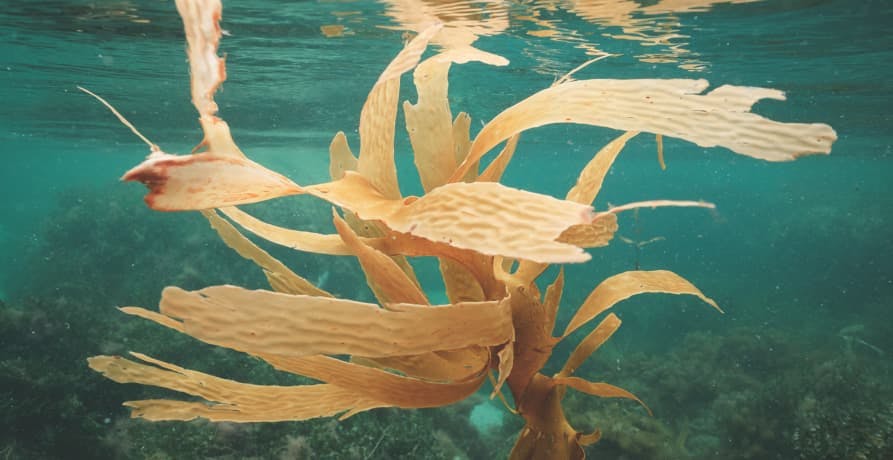

High levels of carbon dioxide in the ocean are also bad news in terms of ocean acidification. The carbon dioxide causes a series of chemical reactions that increase the level of hydrogen ions in the water. The effect of this is that carbonate ions are decreased and the water becomes more acidic in terms of PH.
One of the more significant impacts of this is that certain species, such as coral, plankton, and mollusks, are no longer able to form their shells and skeletons.
Because seaweed farms act as a carbon sink, they are also able to raise the PH of their ocean environment. By reducing the acidity, they support calcifiers (ie. crustaceans), and minimise the risk of coral bleaching.
Seaweed farms are also beneficial in reducing the amount of nitrogen and phosphorus in our oceans. These nutrients have the potential to cause algal blooms, which can be toxic to humans, marine animals, and birds (these algal blooms are known as HBAs or harmful algal blooms).
When algal blooms grow out of control, they deplete the level of oxygen in the ecosystem, which can have devastating effects on marine ecosystems. Lack of oxygen can lead to the formation of dead zones.
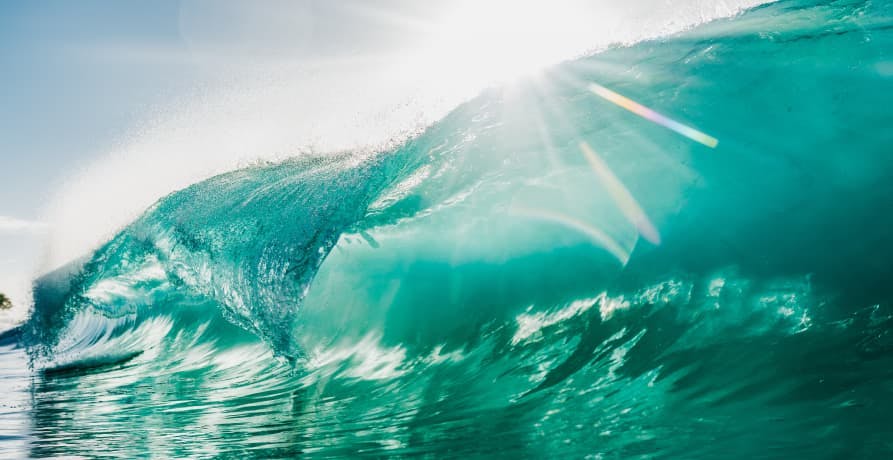

The canopies of farmed seaweed actually soften the impact of waves. By interrupting the energy of the approaching waves, seaweed farms provide a buffer to shorelines and help to minimise coastal erosion.
Seaweed farms act as temporary forests, providing food and shelter for fish and other marine animals. Some studies indicate that when compared to the surrounding area, seaweed farms house over 70% more species.
When the seaweed is harvested, the forest is admittedly lost; however, studies show that marine life is quick to reestablish itself when replanted.

Given the urgent need to reduce our carbon dioxide emissions and to cut our dependence on fossil fuels, researchers and scientists have turned their focus towards climate-friendly biofuels, predominantly made from corn, canola, and soybeans. However, seaweed has attracted increasing attention in recent years for its potential as an alternative source.
Seaweed holds a number of advantages over other biofuel options. Namely because it requires little to no input - ie. it doesn't need fertiliser (which is harmful for the environment), nor does it require water (a growing issue as our world heats up and we experience increasing incidences of heatwaves). Not only this, seaweed farms are incredibly space-efficient - we don’t need to destroy forests or clear land to make way for them.
Seaweed farming also offers a number of more novel environmental benefits. For example, a red variety of seaweed called Asparagopsis has been found to be useful at reducing the methane quantity released in the burps of cattle.
Seaweed farming doesn’t just result in environmental benefits, it also brings with it a variety of other benefits, including:
Climate change is threatening livelihoods across the globe, but perhaps nowhere more so than in our coastal communities. With warming waters, fish stocks are declining and marine ecosystems are being altered forever. Fishing communities and those who rely on the ocean and its produce as a source of income now face an uncertain future.
Seaweed, however, not only actively counteracts the effects of climate change by acting as a carbon sink, but it also provides economic opportunity for communities that have traditionally relied on fish stocks. In many regions where fish stocks have declined, seaweed farming offers an alternative and sustainable source of income, helping to support local livelihoods while protecting marine ecosystems.
Seaweed is a very nutritious food. It contains a number of antioxidants (vitamins A,C, and E). It’s also a source of iodine, which is essential for the functioning of the thyroid. Some varieties of seaweed possess other nutritional benefits - for example, the variety known as purple laver contains B12.
Seaweed has been used in traditional Chinese medicine since at least 300 BC. However, Western medicine also relies on many derivatives of seaweed. Compounds like fatty acids, glycoproteins, alkenes, carotenoids, and ketones are just a few examples of the many chemicals that can be extracted from seaweed for use in medicine to treat health issues such as eczema, cancer, renal disorders, asthma, heart disease, ulcers, etc.
Seaweed is being explored for a number of different applications that not only present interesting business opportunities but also address some of the world’s biggest sustainability and development challenges.
Seaweed has potential for a number of applications across a wide spectrum of industries - including the cosmetic, food, agricultural, pharmaceutical, and energy industries. However, the most headline-grabbing application has been its potential to provide an alternative to plastic wrappers.
Developers have created a seaweed-based coating that could potentially be used in fast-food packaging instead of plastic. It’s possible that seaweed transforms the global packaging industry and helps to solve our plastic pollution problem.
Another issue with seaweed farming is that seaweed is also experiencing the negative effects of climate change. Global warming is causing our ocean waters to heat up, which is impacting the survivability of different species and causing huge upheaval in ocean ecosystems. This means that some regions that currently grow seaweed may find it hard to continue to grow the same varieties in years to come.
This is why, although seaweed farming shows incredible potential in terms of climate mitigation and adaptation, it’s necessary to proceed with caution to ensure that we don’t create any unintended and harmful effects on the environment. It’s also essential that we work to reduce the impacts of global warming and to prevent further climate change.
At Greenly, we help companies navigate the transition to a more sustainable future by measuring, managing, and reducing their environmental impact.
Our suite of sustainability services includes:
| Greenly's Services | What It Means |
|---|---|
|
Carbon footprint assessments
|
Track and analyse your company’s emissions across Scope 1, 2, and 3, gaining insights to manage and reduce your overall footprint. |
|
Life Cycle Assessments (LCA)
|
Understand the environmental impact of your products from raw materials to end-of-life and identify opportunities for sustainable design. |
|
Sustainability reporting support
|
Ensure compliance with key frameworks like CSRD, ESRS, TCFD, and IFRS by preparing clear, data-driven sustainability reports. |
|
Supplier engagement
|
Improve supply chain sustainability by assessing suppliers’ emissions and encouraging low-carbon practices across your network. |
|
Custom decarbonisation strategies
|
Develop tailored action plans to reduce emissions, improve efficiency, and achieve your long-term sustainability goals. |
Get in touch with us today to find out more.