Impacts, Risks, and Opportunities (IRO) for CSRD Reporting
In this article, we’ll break down what IROs are, how to identify and assess them, and what CSRD requires in terms of disclosure.
ESG / CSR
Industries



As many countries and companies around the world set off on their journeys to become more sustainable and transition to the use of clean energy, many countries and companies are considering the use of a wind farm – but is it the best choice for everyone?
In this article, we’ll discuss what a wind farm is, the pros and cons of using a wind farm, and who can benefit from wind farms in their transition to the use of clean energy the most out of anyone.
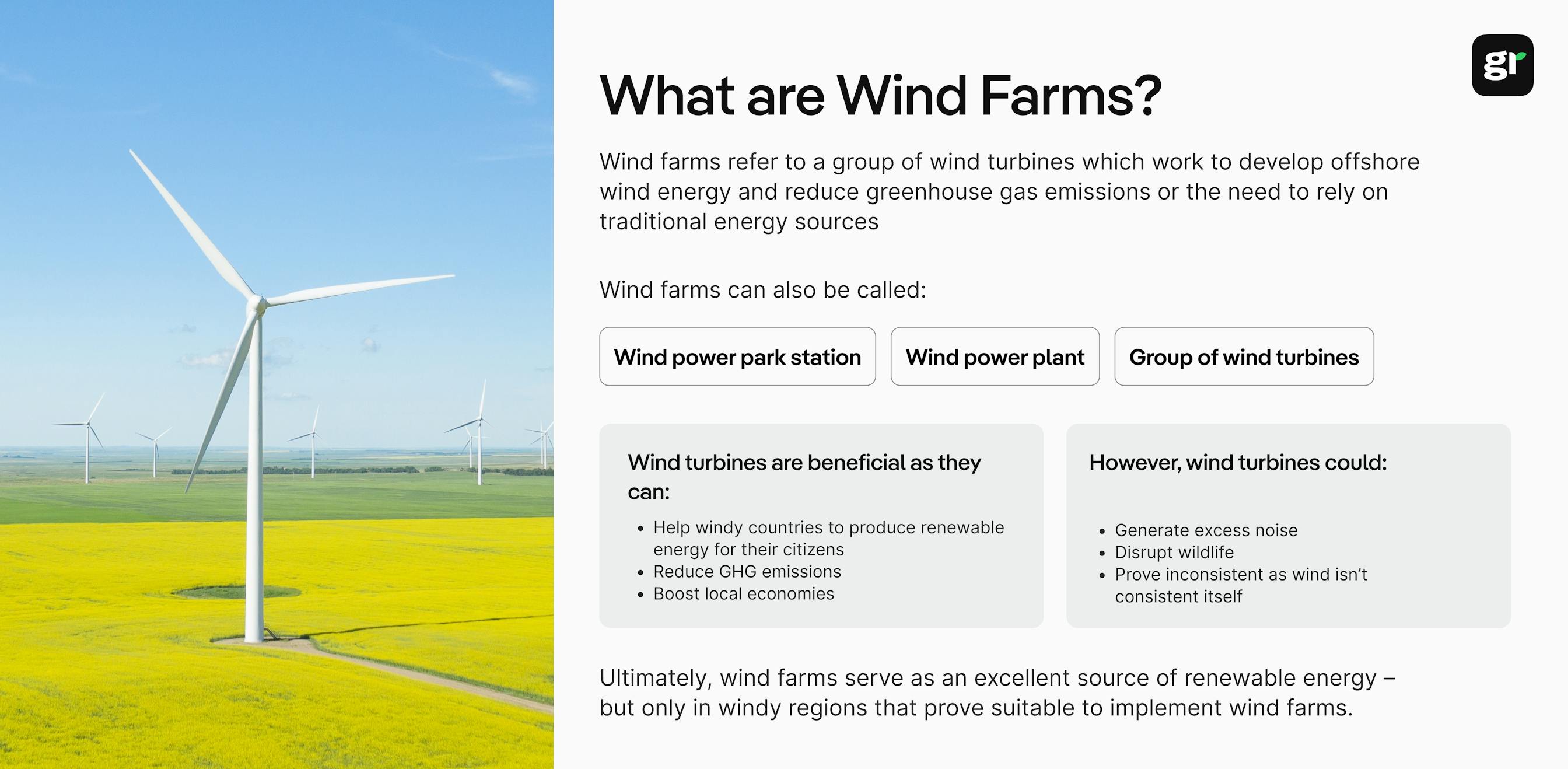

A wind farm is a group of wind turbines within the same vicinity that work together to help produce electricity for nearby areas. Wind farms can vary size depending on how much electricity the wind farm is expected to provide for the surrounding areas.
A wind farm is often also referred to as:
👉 Think of when you’re on a train within Europe or driving across the U.S. and you come across a sea of wind turbines harboring their own section – this is most likely a wind farm. Wind turbines work as wind causes the wind turbine blades, create kinetic energy, and scale wind speed. Typically, utility scale wind ranges from a few hundred kilowatts to several megawatts.
Wind turbines have been skyrocketing around the world and in Europe alone, with countries on the continent such as Germany, France, and Nordic countries like Sweden and Finland installing a whopping 87% of new offshore wind farms – allowing Europe to now possess a 255 GW of wind capacity.
💡 Did you know? As of 2021, the U.S. is in the top five countries having generated the most wind power – having generated a whopping 21% of total world wind electricity generation.
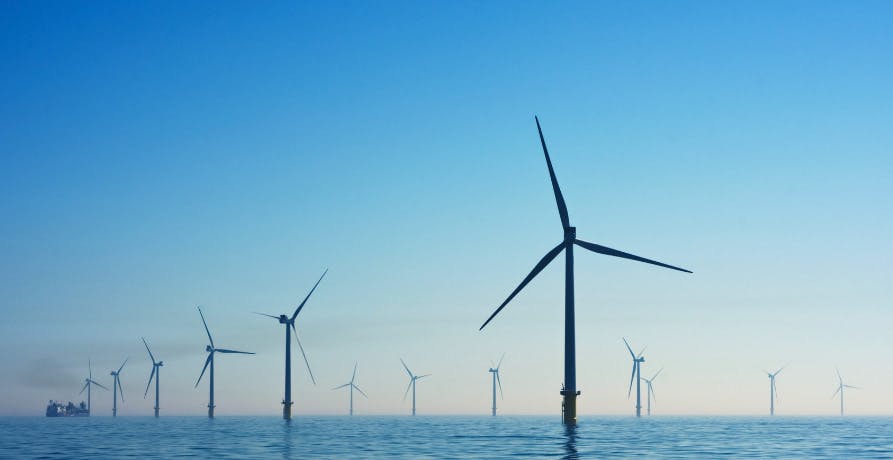

The main principle of a wind farm is to concert the wind harnessed into electricity to be used and to help decrease the dependency on the use of fossil fuels and other finite resources to produce electricity to be consumed by businesses and residences.
Wind farms successfully do this with their propeller-like blades oscillating – acting as a generator that gathers wind to be harvested into electricity.
Remember, wind is ultimately a form of solar energy that is created under three different circumstances:
However, the formation of electricity (or electrical energy) from wind turbines greatly depends on the current wind flow patterns across the U.S. – which is likely to differ depending on the area and how much wind flow there currently is in the area. This is why many countries will try to strategically place their wind turbines or wind farms in an area where there is a substantial amount of wind – which is why countries like Denmark, Sweden, and Finland make use of the high winds their countries get with the use of modern turbines and land based wind energy for country-wide power generation.
In this sense, utility scale wind turbines, wind plants, and today's wind turbines can prove more useful than conventional power plants for regions that receive ample amounts of wind flow.
👉 Wind farms often fare best when they are built on smooth, round hills with open plains and mountain gaps that can allow “wind tunnels” to pass by and for the wind turbines to ultimately harness that “trapped” wind. Also, wind speeds are usually higher when the elevation is above the Earth’s surface: making hills the most productive home for wind farms.
Unbeknownst to most, most of us have made use of wind energy before without noticing it – with the most popular example being when we have sailed on a boat or flown a kite on the beach.
When wind blows, the wind's energy helps to facilitate movement and encourage a rotor diameter or the rotor blades of a mini sailboat to turn – ultimately creating power, movement, and energy to move a sailboat, kite, and even single small wind turbines.
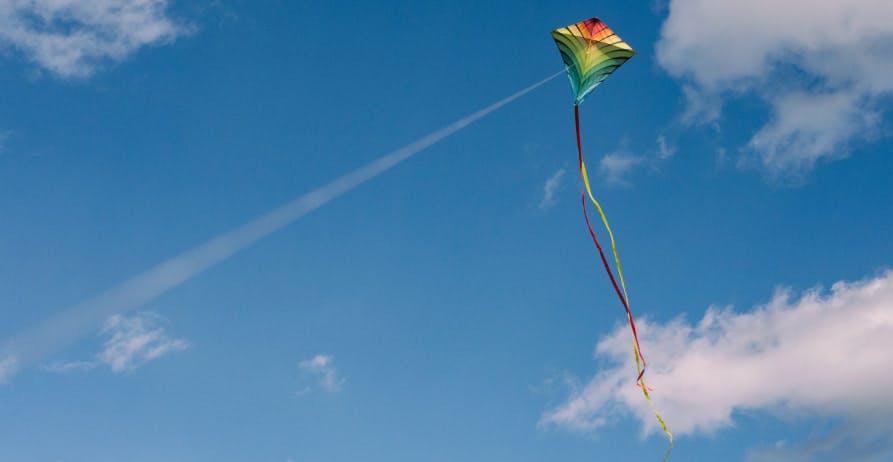

💡Making use of this type of wind flow is also known as motion energy, and is the same type of wind flow that wind farms use to create electricity.
A wind farm works in these six steps:
👉 Remember, the process for horizontal axis wind turbines to turn depend on various capacity factors, even for the biggest wind farm – such as the amount of wind, relevant utility grid, and efforts on behalf of the department of energy or energy information administration to ensure wind turbines are maintained to remain as efficient as possible for energy production.
It's important to note that a wind farm can vary in size from a few dozen to a few hundred wind turbines: meaning that not all wind farms are expected to produce the same amount of energy or prove as economically valuable in the midst of the transition to a clean energy economy. For example, a small wind turbine or a single wind turbine isn't bound to produce as much energy as several horizontal axis turbines generating electricity will.
👉 Currently, offshore wind projects are some of the most popular renewable energy projects taking place around the world: with Nordic countries in Europe coming in full-force with offshore wind farm development, and states in the U.S. like Maryland, Massachusetts, New Jersey, Rhode Island, and Virgina working on new offshore wind farm projects as well to ensure that electricity generated will help to mitigate the negative health effects of traditional energy sources such as fossil fuels and coal.
There are multiple advantages to having a wind farm, such as by helping to improve traditional energy transmission lines, reduce the use of greenhouse gases, help support local communities with clean energy projects, and ensure that the world creates electricity in an eco-friendly way.
Here are a few more ways in which wind turbines and wind farms can prove beneficial for the world:
However, there are also several cons to having a wind farm – such as only proving useful in windy regions, excess noise, or impacting surrounding wildlife.
Here are the differences between wind farms and other forms of renewable energy:
| Energy Source | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Wind Turbines |
|
|
| Solar Power |
|
|
| Geothermal Energy |
|
|
| Hydropower |
|
|

While there are numerous benefits to having a wind farm, there are also some disadvantages:
Given all of the pros and cons of wind farms, are they still ultimately worth installation and the positive attention they have been gaining?

Ultimately, countries with high amounts of wind and smooth hilly areas would benefit most from a wind farm – meaning just because a country is windy, doesn’t mean they have the most optimal conditions for a wind farm. For instance, while the Netherlands may be windy, it’s generally too flat to fully make use of wind farms – as the wind cannot be caught by the wind turbines as easily as they can at a higher elevation.
However, a wind farm could ultimately benefit any country, region, or group of people looking to transition to the use of renewable energy – even if the conditions aren’t perfect, harvesting some sort of renewable energy source is better than acquiring none.
Wind turbines and looking to implement a wind farm are just some of the ways that countries can transition to the use of clean energy – there are so many different ways to harvest renewable energy, it’s worth looking into to learn which one is likely to be most beneficial for your region.
If reading this article about wind farms and their pros and cons has made you interested in reducing your carbon emissions to further fight against climate change – Greenly can help you!
Figuring out the most effective types of renewable energy to use for your company can be confusing, but don’t worry – Greenly is here to help. Click here to schedule a demo to see how Greenly can help you find ways to improve energy efficiency and decrease the dependency on fossil fuels in your own company.
Greenly can help you make an environmental change for the better, starting with a carbon footprint assessment to know how much carbon emissions your company produces.