What is the ozone layer, and how is the ozone layer continuously being impacted by climate change and toxic pollutants being released into the atmosphere?
ESG / CSR
2023-01-20T00:00:00.000Z
2024-09-27T00:00:00.000Z
en-us
It’s easy to look up at the sky, notice the clouds, and think that outer space is just past what is visible to the naked eye – but what is behind the Earthly backdrop is really the ozone layer.
What is the ozone layer, how does it protect humans on Earth, and is the current state of the ozone layer threatened by pollution?
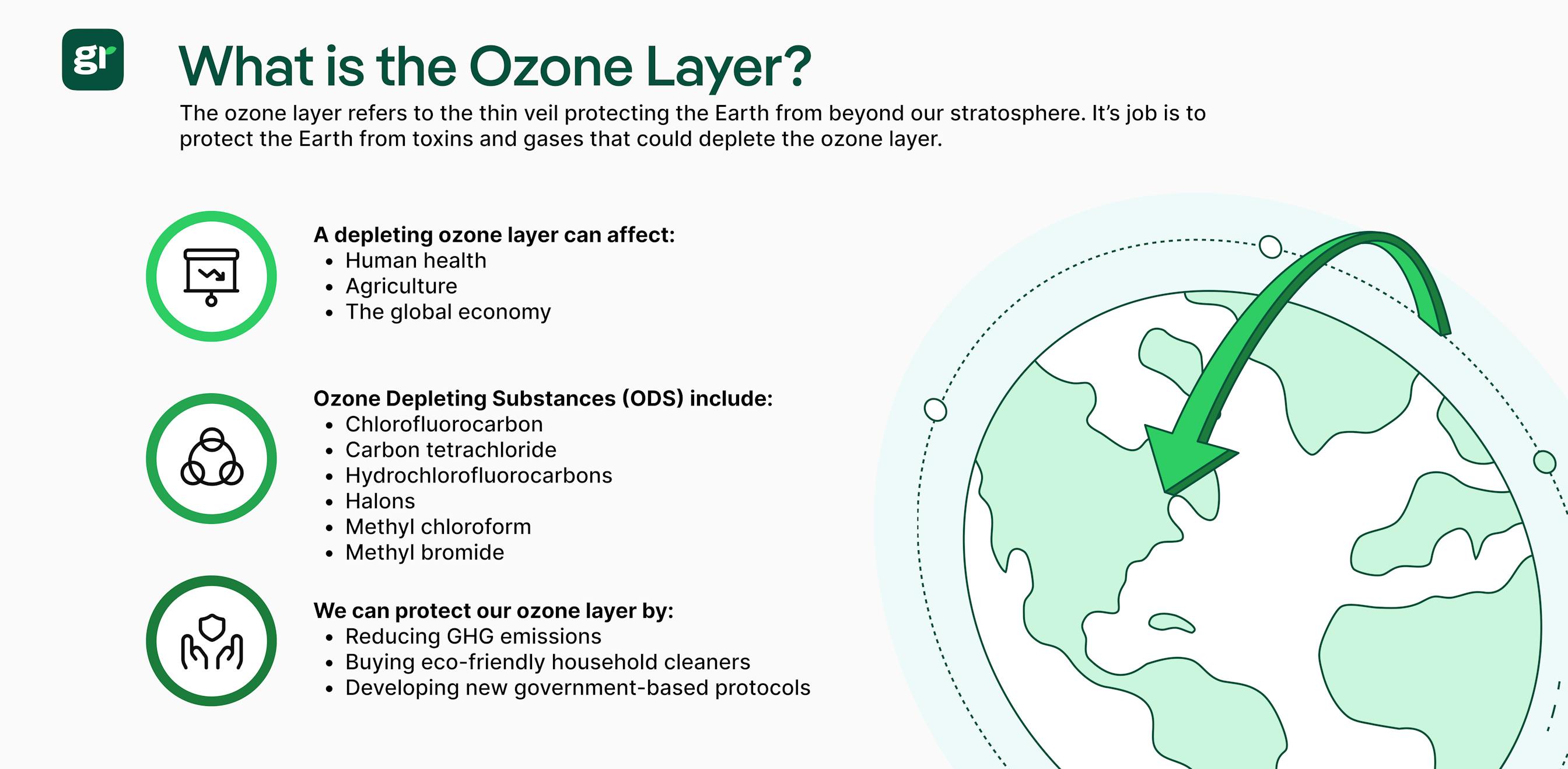
What is the ozone layer?
“The ozone layer is a thin, single layer of the Earth’s stratosphere, and also the second layer of the planet’s atmosphere. As a part of the Earth’s stratosphere, the ozone layer helps to safeguard the planet by providing a shield of natural and protective gasses. The ozone layer may be used interchangeably with the stratosphere – but they aren’t the same thing. Around 90% of the ozone layer exists in the lower level of the stratosphere, whereas the actual stratosphere itself is situated above the Earth’s surface. ”
💡 The ozone layer may be used interchangeably with the stratosphere – but they aren't the same thing. Around 90% of the ozone layer exists in the lower level of the stratosphere, whereas the actual stratosphere itself is situated above the Earth's surface.
The job of the ozone layer is to absorb any potentially harmful ultraviolet rays that come from the sun.
Think of it this way: every time you slather on sunscreen before going to the beach – you are adding an extra protective layer to protect your skin from the sun.
The sun isn't beaming directly onto Earth – the ozone layer is acting as a thin protective layer, very similar to an iPhone screen protector. Even if the ozone layer can't be seen to the naked eye, it is pivotal to protecting humans from UVA lights – which can cause premature aging and skin cancer.
👉 Overall, the ozone layer serves as a thin veil of protection from ultraviolet radiation – but ozone depleting substances (ODS) compromise the health of our atmospheric ozone due to excess greenhouse gases.
What is the current state of the ozone layer?
The ozone layer isn't doing too well – and those of us who live on Earth are to blame, as we contribute to ozone depletion in our daily activities often without even realizing it.
When able to function normally, ozone molecules can regenerate themselves with the help of oxygen atoms. However, the problem is that CFCs, or chlorofluorocarbons, prohibit the air from being able to reform these oxygen molecules with ease – causing the ozone layer to deplete.
“The ozone layer is already thin, accumulating for only around 0.00006 of the Earth’s atmosphere – making it extremely susceptible to further damage. ”
Think of the ozone layer as the difference between someone with thin and thick hair. Someone with thick hair is not as prone to frizz in the midst of a hot summer with high rates of humidity as someone with thin hair is susceptible to the effects of a muggy day. This is because someone with thick hair has thicker individual strands of hair that make it more difficult to penetrate, whereas those with fine hair do not have strands thick enough to block out the effects of humidity. The ozone layer is like someone with thin hair – the ozone layer does not have a thick enough shield to block out the potentially harmful effects of chlorofluorocarbons or other ozone depleting substances.
Relationship between ozone layer and stratospheric ozone depletion
Due to ozone depleting substances and climate change as a whole, the ozone layer is getting thinner – which doesn’t help the ozone layer to accomplish what it needs to do: protect humans from the harmful UVB and UVA rays from the sun. These chemicals deteriorating the ozone layer, called CFCs or chlorofluorocarbons, eat away at the already-thin ozone layer.
The problem is that despite this knowledge, businesses continue to willingly choose the use of CFCs, as they are affordable, aren’t subject to fire hazards, and are unlikely to poison people. However, it’s clear that chlorofluorocarbons are poisoning the ozone layer. CFCs are most commonly found in plastics and refrigerators, making CFCs commonly used amongst people around the world and increasing the chances of CFCs polluting the ozone layer.
👉 Many people refer to the damage in the ozone layer as, “ozone holes” – but this isn’t a scientifically correct explanation. This is because the damage that has been done to the ozone layer resembles more of a patch than an actual hole or "ozone hole". The ozone layer has been damaged due to increased human and industrial activity, which both release ozone depleting chemicals into the atmosphere.

What are ozone depleting substances?
Ozone depleting substances, also known as ODS for short – are toxic pollutants that damage the ozone layer. In addition to making the ozone layer susceptible to damage, ozone depleting substances can also further aggravate climate change – as ozone depleting substances can encourage the surrounding temperatures to spike.
Thankfully, CFCs or chlorofluorocarbons are actively being banned to ensure the future safety and preservation of the ozone layer. Previously used ozone depleting substances are now being replaced by F-gasses – as most ODS substances are now banned throughout the United States.
“Examples of previously used ozone depleting substances include chlorofluorocarbon, carbon tetrachloride, hydrochlorofluorocarbons, halons, methyl chloroform, and methyl bromide. These chemicals are all able to penetrate the Earth's ozone layer and contribute to our thinning ozone layer by reducing ozone concentrations.”
However, it is important to note that ozone depleting substances aren’t entirely obsolete. Those across various sectors in the market can still produce and emit ozone depleting substances as long as the ozone depleting substances are labeled to be used as feed stock in laboratory work. In addition to this limitation, it is important to remain cognizant that while most ozone depleting substances are banned in the United States – they can still be used illegally, such as in mailed packages that would be hard to examine for ozone depleting substances.
👉 Would the ozone layer be in so much trouble if it weren’t for increasing human activity emitting ozone depleting substances?
Here's a breakdown of the different ozone depleting substances:
Ozone Depleting Substances and Their Environmental Impact
| Substance |
Description |
Environmental Impact |
| Chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) |
CFCs are synthetic compounds made up of chlorine, fluorine, and carbon. They were commonly used in refrigeration, air conditioning, and aerosol propellants. |
CFCs release chlorine atoms when they are broken down by ultraviolet radiation in the stratosphere. These chlorine atoms then react with ozone (O3) molecules, causing the depletion of the ozone layer which protects the Earth from harmful UV radiation. |
| Carbon Tetrachloride (CCl4) |
Carbon tetrachloride is a solvent and was used in fire extinguishers, as a cleaning agent, and in the production of refrigerants. |
When released into the atmosphere, carbon tetrachloride breaks down into chlorine atoms, which then contribute to the destruction of the ozone layer, similar to CFCs. |
| Hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) |
HCFCs are compounds that contain hydrogen, chlorine, fluorine, and carbon. They were used as temporary replacements for CFCs in refrigeration and air conditioning. |
HCFCs also release chlorine atoms in the stratosphere, contributing to ozone depletion, though they are less harmful than CFCs. However, they are still being phased out due to their ozone-depleting potential and greenhouse gas effects. |
| Halons |
Halons are compounds containing bromine, fluorine, and carbon. They were used in fire extinguishers due to their effectiveness in putting out fires. |
Halons release bromine atoms upon breakdown, which are much more efficient at destroying ozone molecules than chlorine atoms. Therefore, even small quantities of halons can cause significant ozone depletion. |
| Methyl Chloroform (CH3CCl3) |
Methyl chloroform is a solvent used in industrial applications for cleaning and degreasing metals. |
When released, methyl chloroform is broken down into chlorine atoms, which contribute to the depletion of the ozone layer. Its production and use have been heavily restricted under international agreements. |
| Methyl Bromide (CH3Br) |
Methyl bromide is a pesticide used for fumigating soil and stored products. |
Methyl bromide releases bromine atoms upon breakdown, which are highly effective at destroying ozone molecules. It is now largely banned or restricted under international agreements due to its high ozone-depleting potential. |

Is the ozone layer safe from human interference?
According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, high carbon-emitting human activities are the root cause of continued global warming.
“In other words, human activity is to blame for the negative effects many parts of the planet continue to experience as a result of climate change – including the depletion of the ozone layer.”
💡 The ozone layer wouldn't be in the detrimental condition or fragile state that it is now if it weren't for the uptick in mass production following the industrial revolution.
Space Activity Impacts Ozone Layer Depletion
This proves especially in true, seeing as of June 2024 – the development of new satellites could threaten ozone levels and harm our current ozone shield even more. In fact, the rise in satellites (which could easily turn into space junk and cause even more problems to our stratospheric ozone layer) could contribute to a 650% increase in aluminum based oxide which could also be called ozone depleting substances and prevent the Earth from successfully absorbing UV radiation.
In a similar way that these aluminum based satellites can burn through the Earth's ozone layer, CFCs can deplete the ozone layer when exposed to ultraviolet light as they release chlorine atoms and bromine atoms – which contributes to ozone destruction and overall air pollution.
Household Appliances
If space junk is too abstract a concept to grasp, think of destroying ozone layer and subsequent harmful ultraviolet radiation to the use of refrigerators – which are one of the biggest culprits for excessive use of ozone depleting substances.
Refrigerators and air conditioners weren't commonly used in American households until the 1930s. If common household refrigerators had never come to fruition, and goods weren't being transported across oceans with the need to be kept refrigerated during transit – thousands of ozone depleting substances would've never even had the chance to enter the atmosphere.
👉 Therefore, it's safe to say that the ozone layer is in grave danger due to continued human activity.
Who is affected by the depletion of the ozone layer?
A more-fragile-than-ever ozone layer not only threatens the safety and protection of humans from UV-B and UVA sun rays or continued climate change, but a degrading ozone layer can impact the agriculture sector as well as other forms of life on the planet.
For instance, the aquatic food chain is affected by the depletion of the ozone layer – as when plankton and zooplankton are exposed to UV-B rays, it causes them to die – and throws the rest of the aquatic food chain off balance, ultimately disrupting the surrounding biodiversity.
The depletion of the ozone layer affects a wide variety of species and ecosystems on Earth.
Here are just a few examples of the groups affected by the depletion of our upper atmosphere:
Human Health
As our upper stratosphere continues to deteriorate, more UV light will be able to pass through the clouds and increase the severity of UV rays – which puts people at greater risk for diseases such as skin cancer, cataracts, and other eye diseases.
In addition to this, while vitamin D is known to help boost mood – too much UV exposure can actually weaken your immune system. This can make people susceptible to illnesses and infections as if there were very low temperatures outside.
Wildlife
- Animals – Animals with light skin and fur are subject to suffering from increased UV radiation in the same way humans are more susceptible to skin cancers and eye damage similar to humans are when there is an increase in the sun's ultraviolet radiation.
- Marine Life – UV radiation can penetrate through water and impact aquatic ecosystems, such as phytoplankton – which serve as the base for the marine food web. Therefore, ozone regulation will be needed to protect the aquatic food chain.
- Amphibians – Amphibians are especially vulnerable to UV radiation, as it can impact their development and even cause genetic mutations which put their population at risk.
Ecosystems
- Plant Life – Photosynthesis is good for plants, but too much of anything, even sunlight – isn't good for the nutrient and carbon dioxide cycle of plants.
- Aquatic Life – Reduced amounts of phytoplankton affects not just the food supply but also the carbon cycle, as phytoplankton play a significant role in carbon fixation .
Climate Change
An increase in ozone holes can exacerbate greenhouse gas effects, which can cause further ozone layer depletion. As the ozone layer is made up of three oxygen atoms and occurs naturally, additional ultraviolet light can create polar stratospheric clouds and spur further air pollution.
Global Economy
The risk of increased skin cancer and other UV ray-related diseases can increase global healthcare costs. In addition to this, a depleting ozone layer can cause crops to dry out and affect food supply.
Material Degradation
Increased amounts of sunlight could compromise valuable resources such as plastic, wood, and other useful materials – which could lead to the need for more maintenance and higher operational costs.
Agriculture & Food Availability
It is similar to think of it this way: if there's no ability to resurrect the agriculture sector in the midst of climate change, which are causing excessive droughts and preventing for a fruitful harvest, then the human population won't be able to consume any fruits, vegetables, or grains which are essential to a human diet. In addition, humans won't be able to consume any animal products – as cows can't live without eating grass, which is dependent on a strong biodiversity to grow sufficient food for them.
👉 It's evident that a deteriorating ozone layer can reap negative repercussions for everyone on the planet. However, that isn't to say that changes can't be made to protect the ozone layer moving forward.

How can we protect the ozone layer?
“The ozone layer doesn’t have to keep suffering in silence – they are things that the human race can do to protect the ozone layer from future deterioration. For instance, one of the most surefire ways to ensure the safety of the ozone layer is to implement legislation to continue prohibiting the use of ozone depleting substances and other high-emitting activities. ”
This has already been done successfully before with the Montreal Protocol – which aims to unify the world in the battle against the use of ozone depleting substances. The Montreal Protocol has already seen success – having helped to avoid a 0.5°C rise in global surface temperatures, and is estimated to prevent another 0.5°C rise in global warming by the end of the century. Therefore, while it is vital that people make adjustments in their daily lives to protect the ozone layer – it is also crucial that legislation like the Montreal Protocol remains intact.
However, it is still essential for everyone to take part in their daily lives to prevent the continued depletion of the ozone layer. Government regulation and climate change legislation can make a big difference – but the law can only do so much to prevent the use of products harmful to the ozone layer and climate change in general.
For example, those in the agriculture sector with their own farms can help to protect the ozone layer by avoiding the use of pesticides whenever possible. Customers at the grocery store can make an attempt to be more mindful of their purchases – and opt for local and organic produce whenever possible to ensure they don’t support the use of pesticides.
“One of the easiest and most effective ways that people can contribute to the protection of the ozone layer is to make use of public transportation whenever available instead of gasoline powered cars. This is because the use of gasoline powered vehicles can create excessive amounts of greenhouse gasses that in turn can further contribute to the depletion of the ozone layer. Daily commuters should opt to walk, bike, or use the metro to help fight against climate change and protect the ozone layer. ”
In addition to this, there’s a common culprit in everyone’s household that is more likely than not harming the ozone layer – and that’s cleaning supplies. Many of the name brand household cleaners, such as for kitchens and bathrooms, contain ozone depleting substances that inevitably escape into the atmosphere when you’re cleaning your home – especially if you clean with the windows open.
This doesn’t have to be the case anymore, as many popular cleaning products are now advertised for their use of natural products that won’t cause harm to the ozone layer. These cleaning products may be more expensive than those with ozone depleting substances, but it’ll get the same job done and leave the house smelling fresher given there are no manufactured chemicals.

Lastly, while F-gasses are by no means as detrimental to the ozone layer as traditional ODS are, they are still scientifically proven to trap heat and aggravate climate change. Central air conditioning and heating systems still make use of ozone depleting chemicals from time to time, but there isn’t an excuse for that anymore – with advances in technology and renewable energy, these can be adapted with the ozone layer in mind.
A combination of environmental legislation and human cognizance could do wonders for the ozone layer. All of these are good measures to take to protect the ozone layer, but it’ll only be possible with the help of the government in preventing excessive greenhouse gas emissions in addition to ozone depleting substances from infiltrating the ozone layer.
However, with the government, technology, and the average person making the right choices for the environment – protecting the ozone layer is more than possible.
What about Greenly?
If reading this article about the current state and definition of the ozone layer has made you interested in reducing your carbon emissions to further fight against climate change – Greenly can help you!
Greenly can help you make an environmental change for the better, starting with a carbon footprint assessment to know how much carbon emissions your company produces.