
What are the 3 Pillars of Corporate Sustainability?
In this article, we'll explore what the 3 pillars of corporate responsibility are, why they're important, and how businesses can turn them into practical action.
ESG / CSR
Industries



In recent years, “carbon neutrality” has become one of the most discussed goals in the fight against climate change. But as the term gets tossed around by companies, governments, and even individuals, it’s essential to recognize what it truly means - and what it doesn’t.
In this article, we’ll dive into the meaning of carbon neutrality, why it’s an important goal to work toward, and the practical steps involved in contributing to global climate efforts.
From understanding emissions sources to building a credible commitment, we’ll explore everything you need to know about progressing toward carbon neutrality.
Carbon neutrality - at its core - represents an effort to balance the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) emitted into the atmosphere with an equivalent amount removed or offset.
However, it’s critical to understand that no individual, company, or even country can fully achieve carbon neutrality in isolation. Rather, it’s an aspirational contribution toward a broader, collective goal of reducing global emissions.
Carbon neutrality involves carefully measuring emissions across all activities - from energy use and transportation to production processes - and reducing these emissions as much as possible.
While remaining emissions may be offset through initiatives like tree planting, investing in renewable energy, or supporting carbon capture technologies (CCUS), these methods alone cannot eliminate all emissions.
Instead, carbon neutrality functions as a framework to guide companies and individuals in reducing their climate impact, with a focus on aligning efforts toward global net-zero goals.
It’s also important to distinguish carbon neutrality from a “carbon zero” state, which would require no emissions at all - an extremely challenging, if not impossible, target for most industries.
Similarly, "net zero" often describes a more comprehensive, long-term approach aimed at reducing emissions as close to zero as possible before offsetting the residual emissions that cannot be entirely eliminated.
Here’s a quick guide to understanding the key terms around carbon goals and climate commitments.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Carbon Neutrality | Achieving a balance between emitted and removed CO₂ through measurable reductions and verified offsets. Carbon neutrality supports the global mission to reduce emissions, though no entity can be fully carbon neutral in isolation. |
| Net Zero | A comprehensive approach to reducing all greenhouse gases (GHGs) as close to zero as possible before offsetting residual emissions. Net zero is an aspirational, long-term goal aligned with limiting global warming to below 1.5°C. |
| Carbon Zero | Also known as "zero emissions," this state would mean producing no emissions at all—an ideal but highly challenging goal, especially for industries where emissions are currently unavoidable. |
| Climate Positive | Going beyond carbon neutrality by removing more CO₂ from the atmosphere than is emitted. This approach supports climate resilience and aims to restore natural carbon sinks. |
| Carbon Negative | Similar to climate positive, carbon negative means removing more CO₂ than is emitted, contributing to an overall reduction in atmospheric CO₂. Often achieved through high-impact carbon capture and storage projects. |
The climate crisis - ignited by the Industrial Revolution and driven largely by human-induced carbon emissions - threatens ecosystems, biodiversity, and the stability of our global climate.
By committing to carbon neutrality, individuals, companies, and even entire countries aim to contribute to the global mission of minimizing global warming. Every ton of CO₂ reduced or offset helps slow down climate change’s impact, from rising sea levels to more extreme weather patterns.
The significance of carbon neutrality goes beyond environmental benefits. By reducing emissions, organizations can also benefit public health - especially in cities where high emissions levels often lead to pollution and poor air quality. In this sense, carbon neutrality helps drive positive social impacts, as cleaner air means fewer respiratory issues and healthier communities.
As awareness of environmental issues grows, both businesses and consumers are increasingly mindful of their carbon footprint.
It’s no longer just about selling a product or service - consumers actively want to support companies that show a real commitment to sustainability.
In this way, carbon neutrality influences both companies and consumers, with businesses setting ambitious goals and consumers supporting the companies that align with their ethos.
On a broader level, carbon neutrality has benefits across environmental, economic, and social dimensions. The table below outlines some of the wider impacts of progressing towards carbon neutrality:
| Category | Benefit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental | Reduces greenhouse gases (GHGs) | Contributing to carbon neutrality helps decrease overall greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, supporting global climate targets and helping mitigate climate impacts such as extreme weather and rising sea levels. |
| Environmental | Protects ecosystems and biodiversity | Reducing emissions supports efforts to conserve natural habitats, protect biodiversity, and maintain healthier ecosystems that are crucial for global climate stability. |
| Environmental | Promotes sustainable resource use | Carbon neutrality efforts encourage sustainable practices, such as energy-efficient production and circular economy principles, reducing reliance on finite resources. |
| Public Health | Improves air quality in urban areas | Emission reduction, particularly from transportation and industry, improves urban air quality, helping to reduce respiratory issues, cardiovascular disease, and other pollution-related health risks. |
| Public Health | Supports healthier communities | Cleaner air and reduced pollution contribute to better public health outcomes, fostering healthier and more resilient communities globally. |
| Economic | Attracts eco-conscious consumers & investors | Companies contributing to carbon neutrality align with consumer and investor priorities on environmental responsibility, supporting brand value and long-term growth. |
| Economic | Reduces operational costs through efficiency | Implementing energy-efficient practices as part of carbon neutrality efforts can help lower costs by reducing energy consumption and dependence on fossil fuels. |
| Economic | Stimulates job creation in green sectors | Transitioning toward carbon neutrality drives growth in renewable energy, green technology, and sustainability sectors, creating new jobs and supporting a sustainable economy. |
| Corporate & Social | Reinforces corporate responsibility | Carbon neutrality aligns with a company’s commitment to environmental stewardship, enhancing its reputation as a responsible corporate citizen and increasing accountability in reducing climate impact. |
| Corporate & Social | Promotes transparency and accountability | Carbon neutrality initiatives require transparent emission reporting and reductions, promoting accountability and fostering trust with stakeholders. |
| Corporate & Social | Encourages sustainable supply chains | Efforts toward carbon neutrality often involve working with suppliers to reduce emissions, fostering sustainability throughout the supply chain and promoting environmentally responsible production practices. |
| Global Climate Goals | Aligns with international commitments | Carbon neutrality supports global climate targets, including the Paris Agreement, contributing to a coordinated international effort to mitigate climate change. |
| Global Climate Goals | Inspires community resilience & adaptation | Efforts toward carbon neutrality encourage sustainable community practices, increasing resilience to climate impacts through local conservation, renewable energy use, and sustainable agriculture. |
| Global Climate Goals | Fosters innovation in low-carbon tech | The drive for carbon neutrality fuels research and development in renewable energy, carbon capture, and sustainable materials, accelerating the adoption of technologies essential for a low-carbon future. |
As the urgency to address climate change grows, countries and regions around the world are setting ambitious targets to contribute to carbon neutrality.
These goals aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, advance sustainable practices, and push for cleaner energy sources.
At the same time, a number of standards have emerged to guide companies in their efforts towards carbon neutrality, offering frameworks to measure and manage emissions in a consistent, transparent way.
On a global scale, the Paris Agreement, adopted in 2015, is the cornerstone of international efforts to combat climate change. Under this agreement, 196 countries committed to keeping global warming to well below 2°C above pre-industrial levels, aiming for 1.5°C if possible.
Many countries have since pledged to contribute to net-zero emissions by mid-century, aligning with the Paris goals. This commitment pushes nations to implement policies, foster technological innovation, and collaborate on emission reduction strategies that support a global trajectory toward net zero.
The EU is one of the most proactive regions in setting carbon neutrality goals.
Through the European Green Deal, the EU has committed to working towards the target of becoming the first climate-neutral continent by 2050. This ambitious plan includes legally binding targets to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by at least 55% by 2030 (compared to 1990 levels) and net-zero emissions by 2050.
To support these goals, the EU has implemented policies such as the Emissions Trading System (ETS), carbon border adjustments (CBAM), and strict regulations on energy efficiency and renewable energy use across member states.
These efforts aim to contribute to global net-zero targets through regional and national initiatives.
The UK has established itself as a leader in climate action with its legally binding net-zero target, aiming to reduce greenhouse gas emissions by 100 % by 2050.
As one of the first major economies to enshrine this target into law, the UK government has implemented a series of climate policies under its Clean Growth Strategy. This includes initiatives like phasing out coal, boosting renewable energy production, and incentivizing energy efficiency across industries.
The UK has also introduced carbon budgets, which set legally binding limits on greenhouse gas emissions over five-year periods to keep the country on track.
These policies represent the UK's contribution to global climate goals, supporting the transition toward a more sustainable economy.
Following Donald Trump’s return to office in 2025, the United States has reversed many of its previous climate commitments, including withdrawing from the Paris Agreement under the executive order "Putting America First in International Environmental Agreements," signed on January 20, 2025. This order directs the US Ambassador to the United Nations to formally notify the UN Secretary-General of the withdrawal, which will take effect one year after notification or at a later date specified in the withdrawal notice.
While some states continue to push forward with independent climate action, federal policies now prioritize fossil fuel production and deregulation over emissions reductions. The Trump administration has weakened emissions standards for industries, rescinded environmental justice initiatives, and promoted increased drilling and mining on public lands.
This shift raises uncertainty about the future of national climate policies, though corporate and state-led sustainability efforts remain crucial in driving emissions reductions at a broader scale.
Several internationally recognized standards and frameworks help companies measure, manage, and report their emissions as they contribute to carbon neutrality.
These frameworks provide transparent and consistent methods for companies to track their emissions aligning with global climate goals as part of their collective effort.

Contributing to carbon neutrality requires a structured approach to manage, reduce, and offset emissions as part of a larger, collective effort to limit global warming. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how businesses, governments, and individuals can support the path toward carbon neutrality.
The first step is understanding your emissions. This involves measuring all greenhouse gases produced directly and indirectly, categorized into three main groups:
Accurate measurement is crucial because it forms the foundation for every step that follows. Companies often use specialized tools, like Greenly’s carbon tracking software, to gain visibility over their emissions and identify major sources of impact.
Once emissions are measured, the next step is to cut down as much as possible. This will involve implementing energy-saving strategies, adopting renewable energy, and optimizing processes to become more efficient. Here are some key ways to reduce emissions:
These steps not only contribute to emissions reduction but can also help companies cut costs over time. Note that while full carbon neutrality isn’t attainable for individual companies, each step taken contributes to the larger collective mission.
Greenly offers carbon management solutions to help businesses develop effective strategies to reduce emissions and create a more sustainable supply chain - ensuring that their operations align with their carbon neutrality goals.
After reducing emissions as much as possible, companies can offset their remaining emissions. Carbon offsets involve supporting projects that reduce or capture CO₂ elsewhere, balancing out the emissions that can’t be eliminated. Common types of offsets include:
It’s important to choose verified, high-quality offsets that guarantee long-term impact. Offsets are a means to complement reduction efforts but cannot replace the need for reducing emissions directly.
Greenly offers an extensive catalog of trusted projects, working with the most reputable contribution partners to ensure that companies make a significant, impactful contribution to protecting our planet.


As interest in carbon neutrality grows, so do questions about its credibility, and the potential for misleading claims. Here are some of the key challenges and controversies surrounding carbon neutrality:
Achieving absolute carbon neutrality as a single company is ultimately unattainable. Carbon neutrality relies on balancing emissions with reductions and removals; however, complete equilibrium is a long-term global mission, requiring widespread international cooperation. When companies claim to be “carbon neutral” or on a “net-zero trajectory”, they risk implying that they have achieved complete neutrality. In reality, companies contribute to global net-zero goals rather than achieving them independently.
A truly effective net-zero strategy for companies involves carrying out transformations within the company to align with global carbon neutrality goals. This might include decarbonizing operations, transforming supply chains, and adopting energy-efficient and renewable practices that fundamentally change how the company impacts the climate.
While carbon offsets are widely used to support carbon neutrality goals, they come with significant limitations and potential downsides:
While offsets are a useful complement, they should not replace emissions reduction as the primary strategy. Offsets are most effective when used alongside measurable reductions in emissions and should only cover unavoidable emissions.
Transparency is essential in how companies communicate about their carbon neutrality efforts. Companies should openly acknowledge that they are contributing to, rather than achieving, carbon neutral goals. Public communications should detail achievements and challenges, fostering trust and setting realistic expectations.
Greenly advocates for transparency and accountability in carbon neutrality claims.
Companies should view such goals as an aspirational contribution to global sustainability, rather than an endpoint.
At Greenly, we help clients achieve impactful emission reductions and develop sustainable strategies that align with international net-zero efforts while promoting clarity in communication.
With more organizations and countries adopting net-zero-compatible targets, the landscape for reducing emissions is evolving fast.
Emerging technologies have the potential to reshape how we approach carbon neutrality, though they represent only part of a broader solution.
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is among the more promising developments on the horizon - these technologies aim to remove CO₂ directly from the air or industrial processes and store it underground. While CCS can support emissions reduction in hard-to-abate sectors, it is still in its early stages and will require significant scaling and investment to meet global demand.
In addition, advancements in renewable energy storage and smarter grid management are helping businesses and households more easily adopt renewable energy, reducing their dependence on fossil fuels. These technologies play a vital role in reducing emissions across sectors and provide a sustainable foundation for energy use.
AI and data analytics are also proving invaluable for companies striving to reduce emissions in real-time. Greenly, for example, equips organizations with tools to not only monitor their carbon impact but also pinpoint where improvements can be made. Such solutions help companies make data-driven decisions that align with global net-zero goals, demonstrating how businesses can contribute to collective sustainability efforts.
Consumers today are more informed than ever about environmental issues and are raising the bar for corporate accountability. They aren’t looking for token gestures - they expect transparency and genuine action from the brands they choose. This growing demand has prompted companies to set ambitious net-zero-compatible goals and provide concrete updates on their progress.
Going forward, consumer pressure will likely continue to shape the approach to carbon neutrality. Brands that commit to impactful, transparent sustainability efforts stand to differentiate themselves from competitors. With support from platforms like Greenly, which provides transparent data and actionable insights, companies can align their efforts with consumer expectations and demonstrate measurable contributions to reducing their environmental impact.
Our suite of carbon management services empowers companies to measure, manage, and reduce their emissions, aligning with global climate targets and demonstrating a genuine commitment to sustainability.
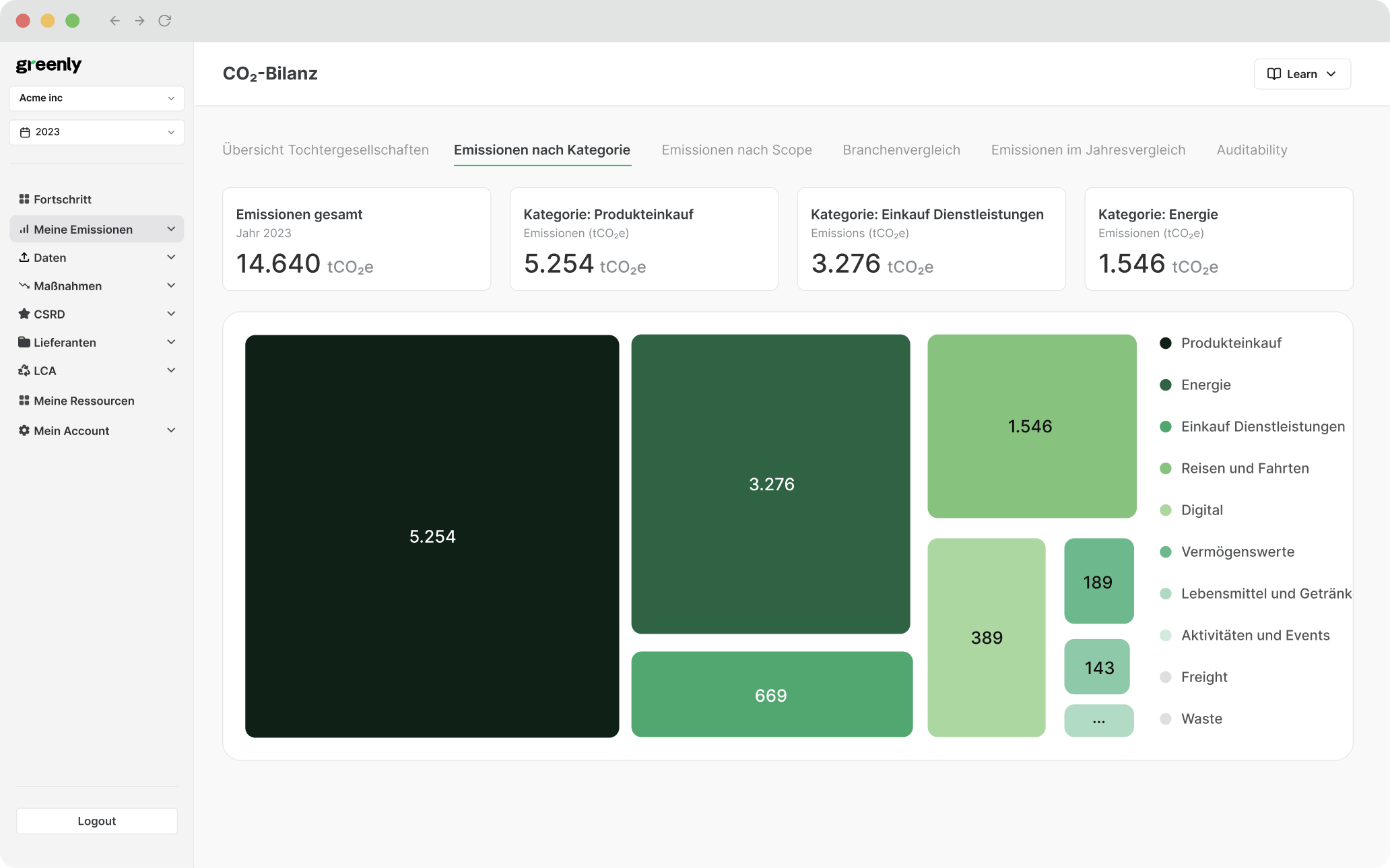
Here’s how Greenly can help your company contribute to net-zero-compatible goals:
Together, we can create a more sustainable future - one where your company not only meets its emissions targets but also contributes to lasting positive change for our planet. Get in touch with Greenly today to start your journey towards carbon neutrality.