ESG / CSR
Industries
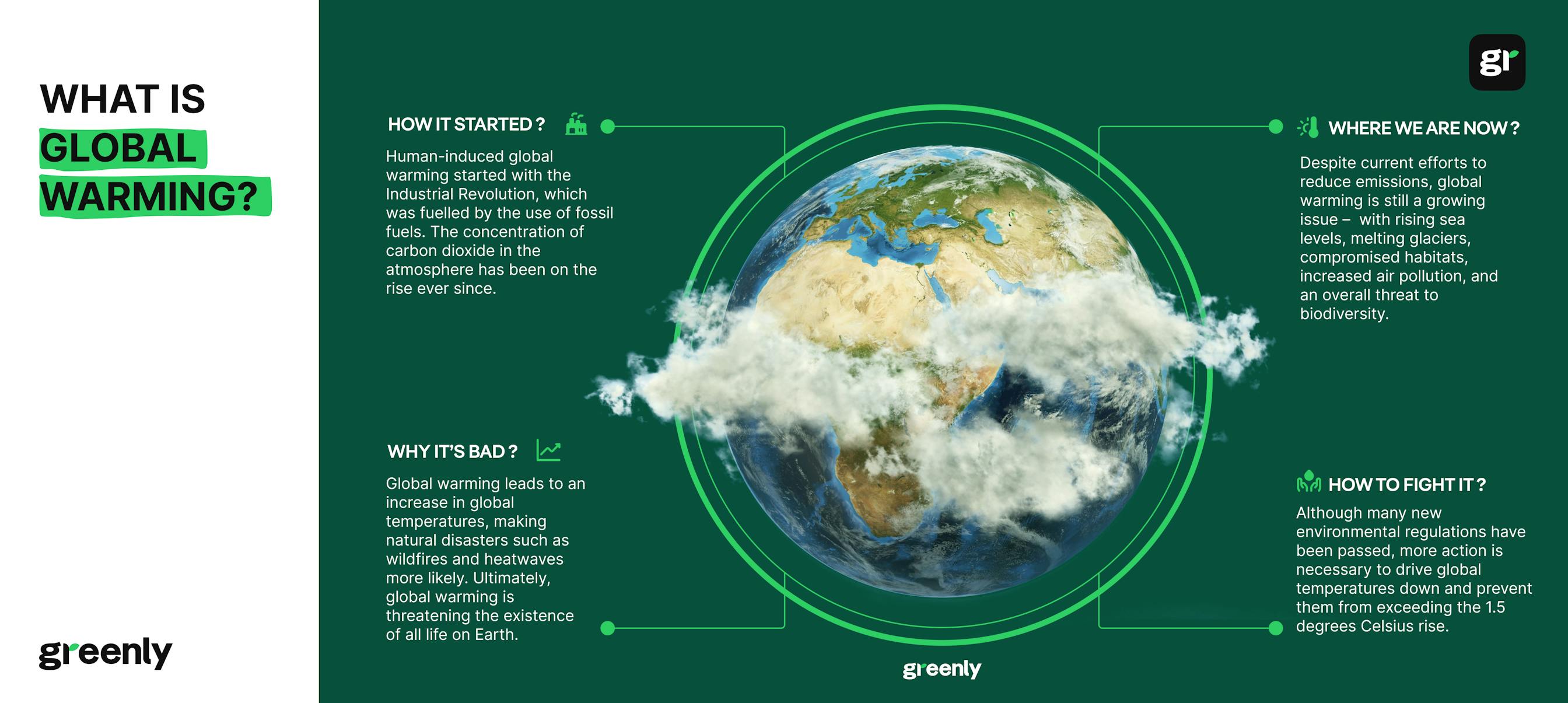
What is Global Warming?



- What exactly is global warming?
- What is the difference between global warming, climate change and climate disruption?
- How did we create such a situation?
- The causes and consequences
- What we can and must do to prevent the worst-case scenario
However, we believe it is important to:
- remind people what global warming is and especially how it works;
- take time to understand the chain of events that has led us to this situation;
- explain why we are currently failing to do what we should do.
What is global warming?
Global Warming, Definition
According to the Oxford Dictionary, global warming is "the gradual increase in the overall temperature of the earth's atmosphere due to the greenhouse effect caused by increased levels of carbon dioxide, CFCs, and other pollutants."
Throughout Earth's history, there have been instances of global warming that had nothing to do with humans – simply because humans didn’t yet exist.
For example, the Palaeocene-Eocene Thermal Maximum (a warming event we know of today) was caused by volcanic activity in that era. However, the rise in temperatures we are currently experiencing in the early 21st century is human-induced.
What is the greenhouse effect?
Some of this energy is absorbed by the Earth's surface, warming it up and causing it to emit infrared radiation. These rays are reflected back to the atmosphere, but are partially trapped by clouds and certain greenhouse gases present in the atmosphere.
This is known as the greenhouse effect. This phenomenon is a vital process for making Earth habitable. Without it, the temperature on Earth would be around -18°C. Thanks to the greenhouse effect, the average temperature is approximately +15°C.
Why are the Earth's Temperatures Rising?
There are two types of greenhouse effects:
In simple terms, the anthropogenic greenhouse effect disrupts the natural one.
Our planet is not capable of absorbing and regulating the amount of greenhouse gases we emit. As a result, they are reaching record levels, not seen in nearly three million years.
And this is not without consequences on global temperatures.
Here are some additional figures.
Since the beginning of the 20th century, global temperatures have risen by 1.1°C, and the 2010-2020 decade was the warmest on record.
While we still sometimes experience extreme cold events (particularly in China, with -48 °C in December 2023), the global trend is a continuous rise in average surface temperatures.
How Did We Get Here?
This is a critical question, especially as we recognise the difficulty of responding effectively to this crisis. Whether political leaders, companies, public figures, or everyday citizens, we are all struggling to take meaningful action.
Many people, particularly in Europe, intellectually agree that addressing climate change is essential. Yet, when it comes to making significant changes in the way we operate, things get complicated from the get-go.
But why is it so hard?
Thus, initiating a true ecological transition, the kind that requires real efforts and choices, means abandoning the societal model that all Western-born generations have known since the end of World War II.
It’s a difficult task for a brain conditioned by habits and instant gratification.
Causes and Consequences of Climate Change
What Causes Climate Change?
Fossil fuels
The extraction and use of fossil fuels is highly polluting.
Damage to Natural Carbon Sinks
Our carbon sinks are damaged to the point where they can no longer perform.
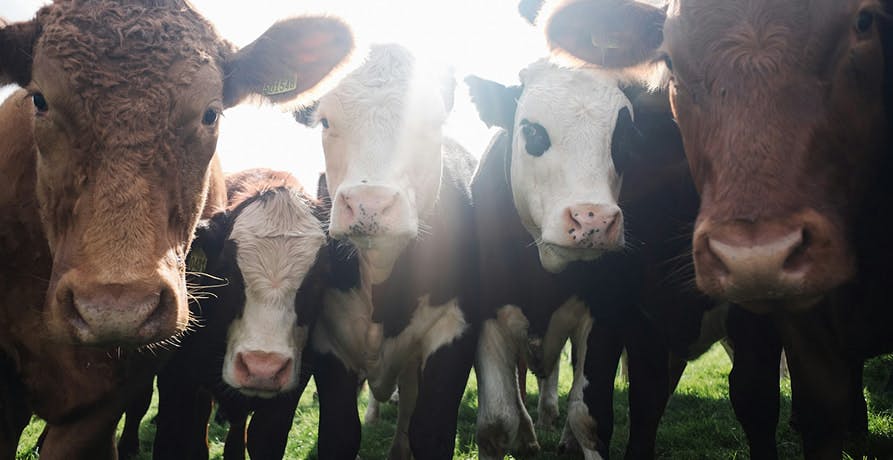
Intensive Livestock Farming
Intensive livestock farming produces greenhouse gases in very large quantities and in many different ways.
Fossil Fuels
Global warming is linked to an excessive concentration of greenhouse gases (GHGs) in our atmosphere.
We produce these gases almost continuously through our activities, most of which depend on the extraction and use of fossil fuels (oil, gas, and coal) present in the Earth's subsoil.
The activities that most heavily contribute to this exploitation are:
- energy production (for electricity and heating);
- fuel production (to power vehicles, planes, and or boats).
What is sadly ironic is that during the Industrial Revolution, our ancestors probably believed that harnessing such energies would lead to societal progress, at a time when comfort was far from what it is today.
We often take for granted conveniences like having hot water on demand but this requires energy.
Worse still, these emissions continue to increase today. Between 2022 and 2023, they rose by a further 1.3%.
To complicate matters further, it is feared that the economic and demographic growth of emerging countries will exacerbate the situation, especially if they adopt the same exploitation models developed by their Western counterparts.

Damage to Natural Carbon Sinks
Carbon dioxide (CO2) has earned a bad reputation, but it's important to remember that we emit CO2 simply by breathing.
Nature, in its original state, had a system designed to ensure that CO2 levels did not exceed what was necessary.
How? Through carbon sinks.
Forests, oceans, and other elements within our ecosystems naturally absorb CO2 as part of their processes, making them "natural carbon sinks".
The problem is that these carbon sinks are now damaged to the point where they can no longer fulfil this function. For example, our forests no longer absorb as much CO2 as they once did. The trees are reaching saturation, and many die in massive numbers during wildfires, which are increasingly frequent due to persistent droughts. When trees die, they release the CO2 absorbed throughout their lives, further exacerbating the problem.
Deforestation only intensifies the issue and is primarily driven by:
Intensive Livestock Farming
Intensive livestock farming produces greenhouse gases in very large quantities (especially methane – CH4), which are released when animals digest their food, but not only.
In practice, greenhouse gases are also emitted when:
- forests are cleared to grow crops for animal feed;
- agricultural machinery powered by fossil fuels is used.
In short, livestock farming is responsible for 14.5% of global greenhouse gas emissions, making it one of the main sectors contributing to global warming.
The FAO (Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations) estimates that 83% of the world's agricultural land is used for livestock.

What Are the Consequences of Climate Change?
1. On the environment
| Consequences | 🚨 Whats happens |
|---|---|
| Rising average temperatures... | leading to more frequent and intense heatwaves. The arid and Mediterranean regions are particularly affected, but they are far from being the only ones. Prolonged droughts impact soils, agriculture, and biodiversity. |
| Melting ice and rising sea levels... | now threaten coastal cities such as Miami, and small island nations such as the Maldives. |
| Disruption of ecosystems... | with land and marine species being forced to migrate or face extinction. This disrupts the natural balance, reduces biodiversity, and creates ripple effects throughout food chains. |
| Ocean acidification... | as carbon dioxide is absorbed by the oceans, it changes their pH levels. Coral reefs, which are home to 25% of marine species, are particularly vulnerable, jeopardising marine biodiversity. |
| An increase in the number, frequency, and intensity of extreme weather events... | such as storms, hurricanes, floods, and wildfires. These events cause loss of life, destruction of essential infrastructure, and even the collapse of some ecosystems. |
2. On society
| Consequences | 🚨 What happens |
|---|---|
| Forced climate migration... | resulting from tensions in host regions, where local infrastructure and resources are often insufficient to accommodate new arrivals. |
| Food insecurity... | caused by droughts, floods, and the disruption of agricultural seasons. This disturbance in food production is a global concern, but its impact is far more devastating in regions that are particularly vulnerable, such as Africa. |
| Resource conflicts... | especially in regions such as the Middle East and North Africa, where water scarcity leads to conflicts between communities and even exacerbates existing tensions. |
| Loss of cultural heritage... | as historical sites and sacred places are no more protected from climate disasters than the rest of the world. The destruction of such sites threatens humanity's cultural legacy and the preservation of certain traditions. |
| Reduced quality of life... | linked to the multiplication of extreme weather events and natural disasters. Whether these have direct (such as increasing indoor temperatures) or indirect (such as resource shortages) effects, they reduce general well-being and cause significant financial losses when disasters damage existing infrastructure. |
3. On health
| Consequences | 🚨 What happens |
|---|---|
| The spread of diseases... | such as chikungunya, as their vectors (mosquitoes) colonise new warmer geographical areas. Regions that were once unaffected, such as parts of Europe, are now at risk. |
| Respiratory issues... | as rising temperatures and air pollution are aggravating tropospheric ozone, which causes respiratory diseases, particularly in children and the elderly. |
| Heat stress... | particularly during heatwaves, leading to a higher risk of heatstroke and dehydration. This is particularly dangerous for outdoor workers, athletes, and vulnerable populations. |
| Mental health deterioration... | caused by extreme weather events and trauma related to property losses, forced displacement, and recurring natural disasters. These exacerbate symptoms of anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in affected communities. |
| Nutritional deficits... | resulting from reduced agricultural yields and limited access to fresh, nutritious food. These deficiencies mainly affect low-income populations, with children and the elderly being most vulnerable to malnutrition. |
4. On the economy
| Consequences | 🚨 What happens |
|---|---|
| Reconstruction and/or rehabilitation costs... | following extreme weather events. For example, the Canadian wildfires of summer 2023 are estimated to have cost nearly a billion dollars. All this spending places a burden on public budgets, hindering other critical investments. |
| Agricultural and wine industry losses... | as climatic conditions affect the stability of crops and incomes, leading to higher food prices. Small producers are particularly affected, as they have fewer resources to adapt to climate-related risks. |
| Increased healthcare costs... | due to the increase in climate-related illnesses. Health systems need to invest more in the prevention and treatment of respiratory diseases, vector-borne illnesses, and stress-related disorders. |
| Losses for the tourism sector... | (such as ski resorts) whose revenue streams are threatened. |
5. Policy
| Consequences | 🚨 What happens |
|---|---|
| Increase in geopolitical tensions... | due to struggles for access to resources. This is the case in the Arctic, for example, where natural resources (oil and gas) are highly sought after. |
| Global governance challenges... | because the countries most affected by climate change (often in the developing world) are demanding more financial and technological support from rich countries. However, the issue of climate responsibility has become central in international negotiations. |
| The emergence of new pressures for adaptation and resilience.... | Governments are called upon to strengthen infrastructure to better withstand natural disasters, which is a significant investment. |
| Strong social mobilisation... | mainly driven by younger generations, who are calling for more ambitious climate actions. These movements influence political choices and have led governments to adopt environmental laws that are not always well accepted by the rest of society for various reasons (as illustrated by the controversy surrounding the carbon tax). |
| A call for a review of current migration policies... | due to the increase in the number of climate refugees. Globally, out of 7.8 billion people, 3.3 to 3.6 billion are considered vulnerable to climate change. |
Have Any Measures Already Been Taken to Fight Climate Change?
Yes, fortunately. Some organisations, in collaboration with many States, have worked to develop solutions aimed at reversing the trend.
In 1988, the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) and UN Environment founded the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), bringing together experts whose mission is to study climate change and develop strategies to stop or mitigate its impacts.
Similarly, the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) was initiated in 1992. At the time, no less than 197 Parties declared their commitment to fighting global warming.
Signed in 1995, the Kyoto Protocol then sought to turn these UNFCCC's commitments into concrete actions. Adopted on 11 December 1997, it led to the establishment of emission thresholds for seven greenhouse gases: methane, sulphur hexafluoride, nitrous oxide, carbon dioxide, perfluorocarbons, hydrofluorocarbons, and nitrogen trifluoride.
However, the Kyoto Protocol proved insufficient, leading to the adoption of the Paris Agreement in 2015. In this agreement, all UNFCCC signatories committed to intensifying and accelerating their efforts, to limit the global temperature rise to +2°C (ideally +1.5°C) by the end of the century.
The most recent initiative? The 2019 European Green Deal, which emphasises the EU's ambition to achieve carbon neutrality by 2050. This commitment has since been strengthened by the "Fit for 55" climate package, enacted in 2021.

Should We Focus on Mitigation or Adaptation to Global Warming?
How Can We Fight Global Warming?
In broad terms, the most urgent priority is :
- to reduce our carbon footprint as quickly and efficiently as possible;
- to protect the systems that can facilitate this (complex) societal transition.
Whether on an individual or organisational level, many initiatives can contribute to this collective effort. It is also important to take into account the fact that we are not all in the same boat when it comes to ecological transition.
The same goes for companies: depending on their industry, the challenges they face may vary. But somehow, this is not what matters.
What’s important is that everyone moves in the same direction, working to reduce their environmental impact with the resources available to them.




