ESG / CSR
Industries
What is Ecodesign?



- What eco design is and how it works
- How LCA is related to Ecodesign
- The importance of ecodesign across all industries
If we want to adequately fight against climate change, we need to alter everything we do – from the way we eat, travel, and even the way we develop and build infrastructure, and this is where ecodesign comes in.
Ecodesign refers to the method of designing a product or service with the environment in mind, meaning that the product would seek to reduce its environmental impact, promote sustainability, and increase overall business with an improved life-cycle.
In this article, we’ll explain what ecodesign is, what the main goals and benefits are, examples, and why we should all get involved with ecodesign.
What is the Definition of Eco-Design?
Ecodesign is the approach to drafting and constructing a building with the environment in mind. This means that the potential design should seek to incorporate environmental aspects into the design to either avoid or directly reduce its environmental impact on the surrounding area.
Seeing as construction and buildings are the backbone or setting for many of our daily activities, a concept such as ecodesign is crucial to reducing our environmental impact on a global scale long-term – making it an all-in-one approach to sustainable development.
The main goal of ecodesign is to reduce the environmental impact that a product, service, or building has on the planet – such as by taking raw materials, sustainable materials, life cycle assessment, and other environmental considerations into account when developing a production model.
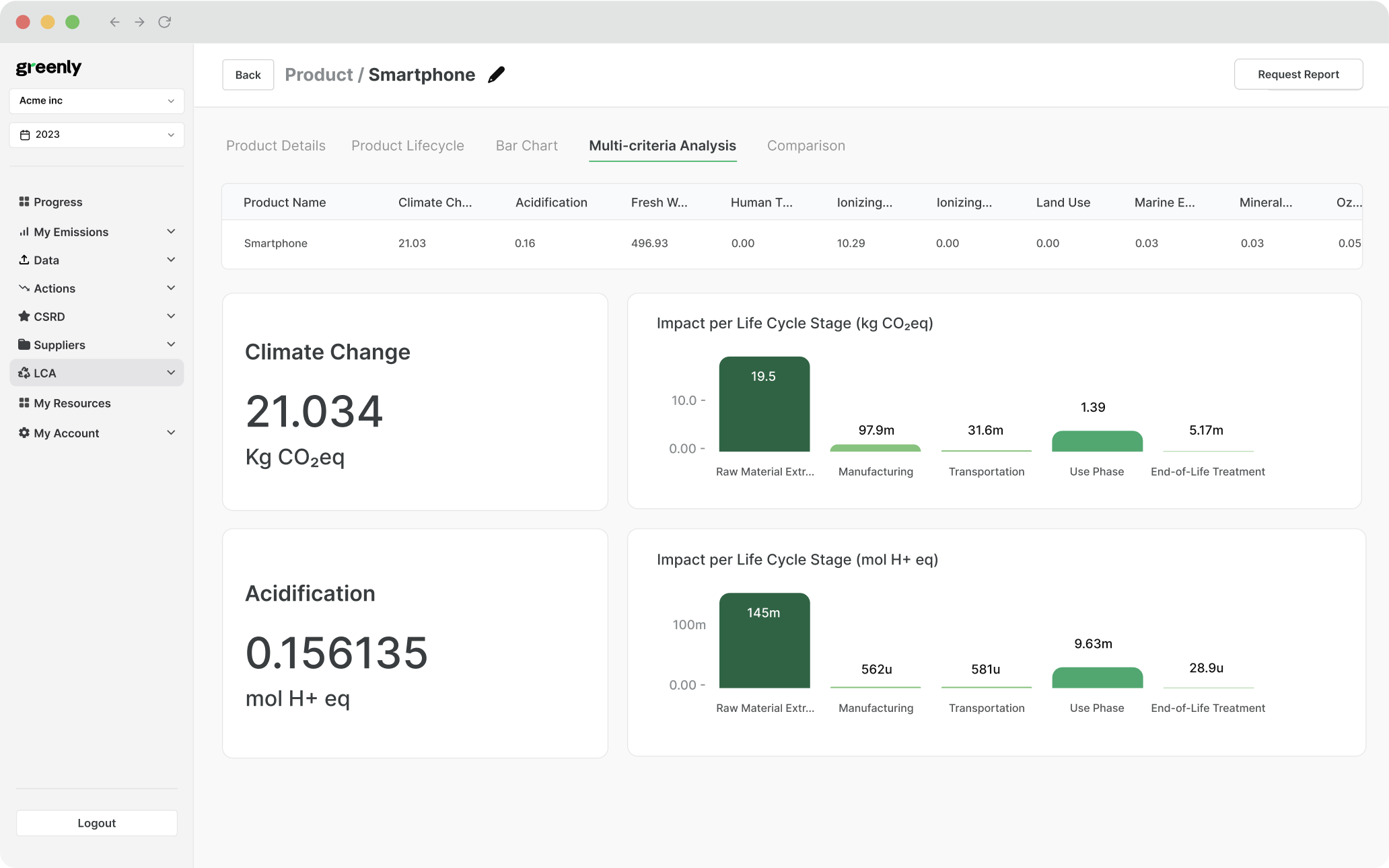
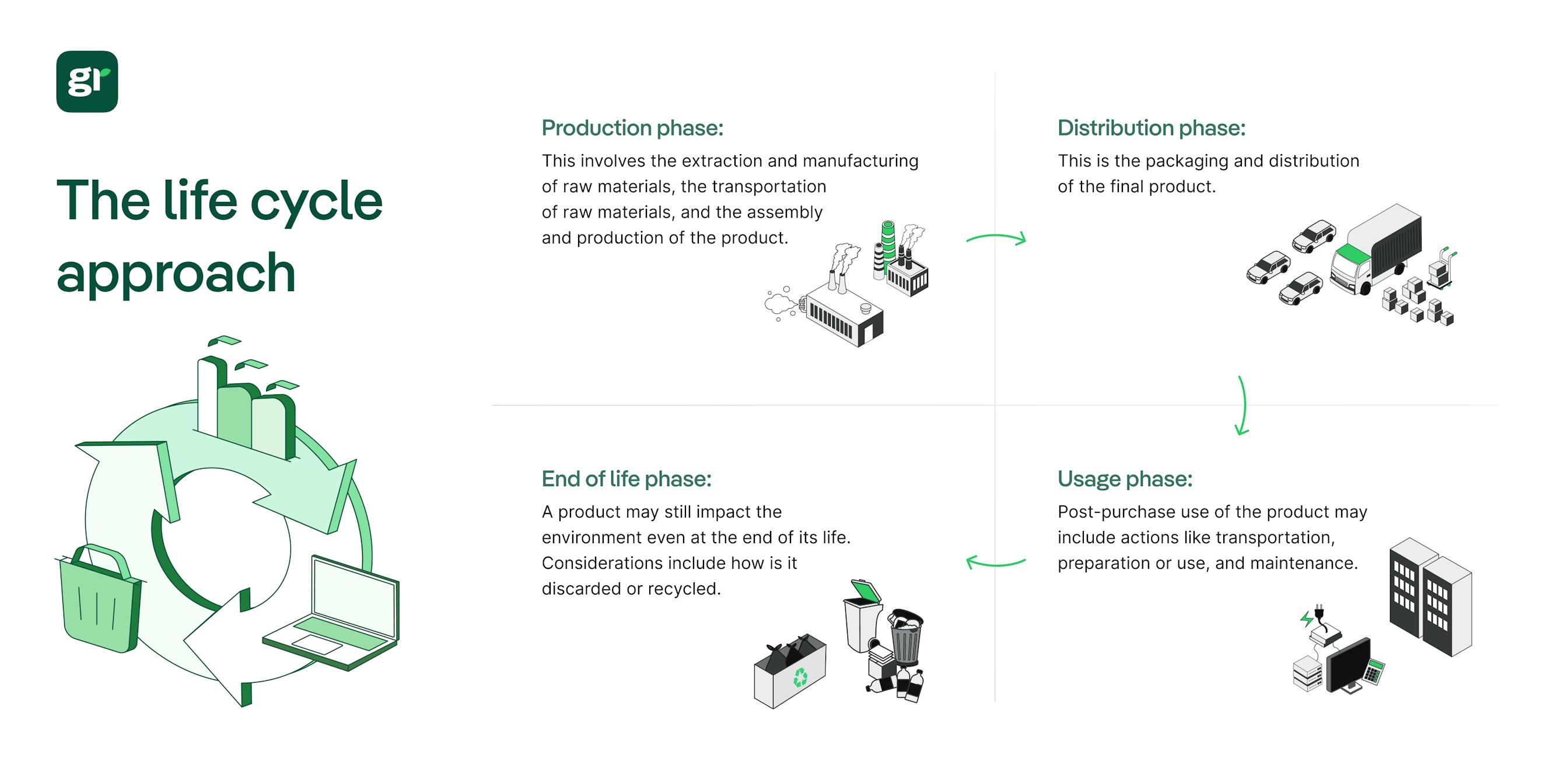
Importance of Life Cycle Analysis For Ecological Design
According to the Environmental Impacts Academy, life cycle analysis is a crucial component in any eco design approach, as both the entire lifecycle and end of life analysis can provide useful information on how to use different material and ensure less energy is emitted from a product or service.
The timeline of the four phases of a product's life cycle will break down how a product's life cycle is imperative in an organization's ecological design:
1. Raw Material Extraction 🌍
Emissions come from mining, harvesting, and transporting raw materials like metals, plastics, or natural fibers.
Ecological Design: Source recycled or renewable materials to reduce carbon output at the start.
2. Manufacturing 🏭
Energy-intensive production processes and chemical treatments often release large amounts of greenhouse gases.
Ecological Design: Improve energy efficiency and use cleaner production techniques or local facilities.
3. Use Phase ⚡
Some products (like electronics or appliances) consume energy or resources during their use.
Ecological Design: Make products energy-efficient, modular, or longer-lasting to reduce emissions over time.
4. End of Life ♻️
Products discarded in landfills or improperly recycled release methane or contribute to pollution.
Ecological Design: Design for disassembly, recyclability, or compostability to ensure sustainable disposal.
Ultimately, any product, service, or building with ecodesign should have made the necessary adjustments to prove just as useful as before while aligning itself with the sustainable needs of today.
Environmental Impact of Product Design
Some of the key things to remember when seeking to ecodesign a product or service includes:
- Conducting a Life-Cycle Assessment for the product;
- Seeking to extract raw or ethically sourced materials;
- Revamping traditional production processes to be more sustainable;
- Considering if a product can be recycled, how it is usually disposed of, and how easily it can be repaired to prevent the consumer from tossing it sooner than necessary;
- Reducing the amount of pollutants used during the industrial process.
It is important to remember ecodesign is a continuously evolving concept, and is meant to be used as a genuine approach to transform the way we use design as opposed to being used for greenwashing or marketing purposes.

What is the Difference Between Green, Sustainable, and Ecodesign?
Ecodesign primarily refers to the development and creation of a product without causing excess environmental damage, whereas green design predominantly deals with creating energy efficient products or infrastructure and sustainable design is garnered towards improving the performance of a building while mitigating excess environmental harm.
The battle cards below will breakdown the differences between green design, sustainable design, and ecodesign and how they each benefit the circular economy:
In a sense, ecodesign is a more simplistic term than green or sustainable design – as the latter two options have more specific goals and criteria than ecodesign does.
If you’re still confused on the difference between eco design, green design, and sustainable design – here is a breakdown of green design and sustainable design in order to better understand what sets them apart from ecodesign.
Green Design
Green design specifically aims to improve the energy efficiency of a product, service, or building. While this type of design also helps to ultimately help the environment, green design will require the designer to primarily seek ways to improve the battery life or energy usage of their proposed project or idea.
As a result, green design will also require careful consideration when choosing which materials to use and to make the product just as useful without depleting natural resources. Therefore, green design can help to reduce fuel consumption and ensure efficient use of a product or service.
Sustainable Design
Sustainable design is primarily focused on reducing the detrimental impact a building has on the planet – while also seeking to improve the performance of the building.
This usually involves seeking to implement green building ideas, such as by adding green roofs, finding ways to reduce water usage, and considering the type of materials used during construction.
Ultimately, the main goal of sustainable design is to prevent using non-renewable resources in order to reduce waste and curate a building that can be used by society and future generations in a more sustainable manner.
Regardless of whichever type of design you choose, opting for ecodesign, green design, or sustainable design can all help to improve the economic viability of an infrastructure while also reducing the environmental impact of a building.

What Are the Benefits and Disadvantages of Ecodesign?
There are many benefits associated with ecodesign, such as helping to reduce operational costs, cultivating better customer and supplier relationships, and the development of more functional and sustainable products. However, there are also some disadvantages to ecodesign – such as a lack of consumer awareness on the importance of ecodesign and advertising the product to the appropriate demographic.
Many people will opt to use ecodesign not only because it can help benefit the environment, but because ecodesign can help to slash business costs and ultimately help a company to be more profitable – seeing as consumers are becoming increasingly aware of the importance of purchasing or investing in more sustainable products.
The summary cards below will summarize the benefits and disadvantages of ecodesign:
🌱 Benefits of Eco Design
- Reduced production costs and improved efficiency
- Less reliance on non-renewable materials
- Better cost savings through streamlined resourcing
- Avoided disposal costs and reduced landfill impact
- Improved product functionality and quality
- Encourages product sharing across markets
- Mitigates emissions, aiding climate strategy
- Promotes better working conditions for employees
⚠️ Drawbacks of Eco Design
- Lack of consumer awareness on eco design value
- High upfront costs despite long-term savings
- Marketing difficulties for redesigned products
- Resistance to change due to perceived risk
- Challenges integrating into existing systems
- Complex life-cycle analysis for accurate use
Ultimately, ecodesign can also help companies to expand their business, increase their sales revenue, or reach their financial goals seeing as ecodesign indirectly helps to improve the energy efficiency or sustainability of a product, service, or building.
Here is a breakdown of the pros and cons of ecodesign:
Pros of Ecodesign
- Reduced production costs;
- Improved efficiency of products;
- Lessened need to source non-renewable materials;
- Increased cost savings seeing as less labor and resourcing of materials is needed;
- Avoided disposal costs and less contribution to greenhouse gas emissions in landfills;
- Improved products in terms of functionality and quality, such as with new generations of the iPhone;
- Improved chances at the product being shared amongst the market;
- Mitigated emissions which help to improve the environmental performance of the product and ultimately its relevance in the midst of climate change;
- Better working conditions for employees which are a part of the product being subjected to ecodesign.
Ecodesign can also help to inspire companies to develop new products or services that would have never come to mind without the implementation of ecodesign in the first place.
The flip cards below will reveal some examples of eco-design leads to products or services that might that have been developed otherwise:
However, there are still many challenges that designers may come across when seeking to utilize ecodesign.
Cons of Ecodesign
- A lack of understanding on the importance of ecodesign amongst customers, which may deter them from purchasing the product or recognizing its value;
- Upfront costs to alter the production or materials used in the future ecodesign, and while this is usually more cost-effective in the long-run – many in the company may be hesitant to take this step;
- Hardships in advertising the new ecodesigned product may prove difficult if the original demographic no longer finds the optimized or re-designed product appealing;
- Risk factors in trying to ecodesign a product that has already been financially successful, referring to the “if it ain’t broke, don’t fix it” motto;
- Challenges in incorporating ecodesign into already existing and popular products;
- Difficulty in correctly analyzing the life-cycle analysis of a product to utilize ecodesign to its full potential.
The drop down sections below will provide a few real-life examples of struggling to overcome the challenges of eco-design:
However, overcoming the barriers can lead to more advanced, profitable and sustainable products.
Even if the challenges of ecodesign may seem intimidating or risky to a business, making an effort to overcome these obstacles and eventually reaping the benefits of ecodesign is usually worth the initial struggle and investment – in terms of time, finances, and the positive environmental effects.

What Are Some Examples of Ecodesign?
Examples of ecodesign include using less materials, improving the recycling process of the product, ensuring the product creates less emissions than its predecessor, and developing innovative products which can be shared to further promote the importance of sustainability.
The good thing about ecodesign is that it can be used in a wide-variety of ways, and it is not necessary to incorporate all examples of ecodesign to have a product be considered an ecodesign – developers and designers can take the ideas most relevant and effective to be used for their future ecodesign.
The flip cards below (move cursor over card to flip) will reveal some examples of products with ecodesign that you may unknowingly use in your everyday life:
Additional Examples of Eco Design
More examples of ecodesign include:
- Using Less Materials: The phrase, “less is more” is a pivotal component to the concept of ecodesign. This is because seeking to use less materials can result in fewer emissions and energy usage over the long-term.
- Reducing Emissions & Energy Consumption: Products that reduce energy usage, improve energy efficiency, or help to lower overall emissions are examples of an ecodesign.
- More Recyclable: If a product can be more easily reused, recycled, or disposed of more safely – it can be considered an ecodesign. Think of pieces of technology that can be easily removed into separate parts to be refurbished into new gadgets.
- Seeking to Use Eco-Friendly Materials: Aiming to use biodegradable materials, even if it’s just in the packaging of your product, can make a huge difference.
- Long-Term Value: One of the main points of ecodesign is to create a product that can stand the test of time. Therefore, if the product can be used multiple times without being worn down easily – it can be considered an ecodesign.
- Creativity: Ecodesign usually requires “out of the box” thinking. If a product utilizes innovative thinking to push sustainability forward, it falls under the category of an ecodesign.
- Spreads the Word: Think about it: if your friend has a cool ecodesigned product, such as a solar powered iPhone case – it will make you want to buy one, too. Therefore, a good ecodesign will usually intrigue others to learn more about the product and incentivize them to purchase their own eco-designed gadgets.
Ultimately, an ecodesign can be used for all sorts of things – from a toothbrush, tupperware, jackets, building insulation, sustainable offices, technology, furniture, and more.

Why Should All Businesses Consider Ecodesign?
We should all seek to use ecodesign as it can help to improve the prosperity of our businesses, encourage greater productivity in our daily lives, reduce our environmental impact, and encourage greater creativity when designing products, services, or infrastructure.
Ecodesign can truly be used by anyone and everyone, regardless of their profession or sector – it's a concept we can all use and benefit from.
There are several reasons why we should all consider ecodeisgn. For starters, we’re living in a world suffering the effects of climate change – and one of the easiest ways to keep the dramatic effects of a warming world is by altering the products and services we use in our everyday lives, which can be done with ecodesign.
The drop down sections will reveal additional reasons why we should all take ecodeisgn into account:
In addition to this, ecodesign helps with resource conservation, cost savings, meeting consumer demands, and can help companies comply with current environmental regulations.
At the end of the day, ecodesign isn’t just a way to help the planet or help your business – but to build a more sustainable future where we will continue to have a platform to make our creative ideas come to life.
Essentially, if we don’t get into ecodesign now – it will become more difficult overtime to address our environmental and societal challenges. Ecodesign can help us conquer them today while still leaving room for creativity and consumerism.
What About Greenly?
If reading this article about ecodesign has made you interested in reducing your carbon emissions to further fight against climate change – Greenly can help you!
Seeking to understand how ecodesign could have an impact on your business may seem difficult, but don’t worry – Greenly is here to help! Click here to book a demo and get personalized expertise on how you can start to reduce your own emissions and decrease your environmental impact.
Greenly can help you make an environmental change for the better, starting with a carbon footprint assessment to know how much carbon emissions your company produces.