ESG / CSR
Industries
Is Water Vapor a Greenhouse Gas?



- Definition of water vapor
- Detailed breakdown of the water cycle
- How to reduce water vapor in the atmosphere and its impact on global warming as a whole
In today’s society, next to everything we do contributes to greenhouse gas emissions – leading some people to wonder how water vapor is a greenhouse gas that also contributes to global warming.
Water vapor refers to water in its gaseous form when it is below boiling temperature – such as with a boiling teapot where the excess steam evaporates into the air. However, most people do not realize that this is a consequence of climate change.
In this article, we’ll review what greenhouse gasses are, how is water vapor a greenhouse gas, and how we can reduce the amount of water vapor contributing to global warming.
Recap: What Are Greenhouse Gasses?
Greenhouse gasses, also referred to as GHG emissions, refer to the heat trapped in the atmosphere as a result of excessive industrial activity.
Greenhouse gasses are one of the main contributors to global warming, as it contributes to the greenhouse gas effect that is contributing to climate change itself.
Examples of Greenhouse Gasses
Some examples of greenhouse gasses include:
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂)
Methane (CH₄)
Nitrous Oxide (N₂O)
Industrial Gases
Hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs)
Perfluorocarbons (PFCs)
Sulfur Hexafluoride (SF₆)
Nitrogen Trifluoride (NF₃)
Although common in our daily lives as a result of increased aviation travel, industrial processes, and single use products – it is important for all of us to remain cognizant of the effects of greenhouse gas emissions and how they continue to affect our environment.
Unbeknownst to most, water vapor is the most abundant greenhouse gas – despite the fact that many scientists believe that water vapor produced by humans has an impact on the amount of water vapor greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere.

What is Water Vapor?
Water vapor, most often referred to as steam, is water in its evaporated state – which is when water vapor mixes with the surrounding air and “disappears” before your eyes.
However, in reality – that water vapor increases not only humidity, but the temperature of the surrounding air. This is often why many people will choose to open a window when taking a shower or ensuring proper ventilation in the kitchen to avoid a room from getting too hot and humid.
The most common example of water vapor refers to steam, such as a boiling pot of water where water vapor then escapes from the pot into the surrounding air.
Most people are unaware how things like water vapor on its own can be contributing to climate change, making it more important than ever before to educate ourselves on all the ways we can work together to save the planet.
Check out our podcast below to learn more about this:
Examples of Water Vapor
Some examples of water vapor include:
Steam
From boiling water, hot showers, or saunas — steam is the most familiar everyday form of water vapor.
Clouds & Fog
Gray mornings form when water vapor condenses into tiny droplets, creating low clouds and fog near the surface.
Exhaling in Cold Weather
Your breath’s moisture condenses in chilly air, making water vapor visible as a small cloud.
Humidity
On humid days, there’s more water vapor in the air — why the air feels “wet” and heat can feel heavier.
Evaporation from Lakes & Oceans
Sunlight drives evaporation over large waters — a process tied to rising sea levels and broader climate patterns.
Plant Transpiration
Plants release water vapor through tiny leaf pores, adding moisture to the air and fueling local cloud formation.
Overall, water vapor is essential for the water cycle and is a massive contributor in greenhouse gas emissions.
What is the Water Cycle?
The water cycle refers to how water can shift between various states of matter, such as a solid, liquid, or gas. It is important to note that water is the only substance on Earth that can easily change from one state of matter to another, and as a result – water vapor
Remember, when it comes to how water vapor affects climate change, it is detrimental when in a gaseous state of matter.
The vertical timeline below will reveal how ater can change into various states of matter:
1). Melting 🧊➡️💧
The process where solid water (ice) changes into liquid water as heat is absorbed.
2). Evaporation 💧➡️💨
The transformation of liquid water into water vapor as it gains heat energy.
3). Condensation 💨➡️💧
The process where water vapor cools and changes into liquid water, forming droplets.
4). Freezing 💧➡️🧊
The process where liquid water changes into solid ice as it loses heat.
5). Sublimation 🧊➡️💨
The transformation of solid water (ice) directly into water vapor, bypassing the liquid phase.
All of these changes require a transfer of energy, as regardless of the state of matter the water is currently in – the water particles must be absorbed or released to evolve into another state of matter.
In the event of how water vapor can act as a greenhouse gas, the transfer of energy on behalf of the water particles creates heat – which is why water vapor and evaporation can be classified as a greenhouse gas itself.

What is the Global Warming Potential of Water Vapor?
The global warming potential of water vapor is catastrophic, seeing as water vapor remains one of the most abundant and powerful greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere.
However, it is important to note that water vapor doesn’t have the same fixed GWP as other greenhouse gasses.
According to a study by IOP science from September 2018, the global warming potential (GWP) of water vapor is H2O of −10−3 to 5 × 10−4 – which in simple terms, means that larger increases in water vapor emissions would have a small impact on global warming.
Therefore, water vapor doesn’t have a fixed GWP in the same way as other greenhouse gasses such as carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), and nitrous oxide (N₂O). Regardless, the impact of water vapor greenhouse gasses is still worthy of our attention.
The interactive flip cards (move cursor over card to flip) will reveal why water vapor can still have a reasonable impact on global warming and helps us to understand the increase in atmospheric temperatures:
Overall, water vapor doesn’t have a set GWP in the way other greenhouse gasses do – but it can amplify the effect of other greenhouse gasses in the atmosphere, making it important in terms of reducing the negative impact of the greenhouse effect.

How to Reduce the Amount of Water Vapor in the Atmosphere?
Drying out the atmosphere from excess water vapor would be one effective way to reduce global warming, as water vapor exacerbates the greenhouse effect.
One idea to mitigate the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere would be to “freeze dry” the excess water vapor – which would be done by turning it into ice below the stratosphere where the air is the coldest.
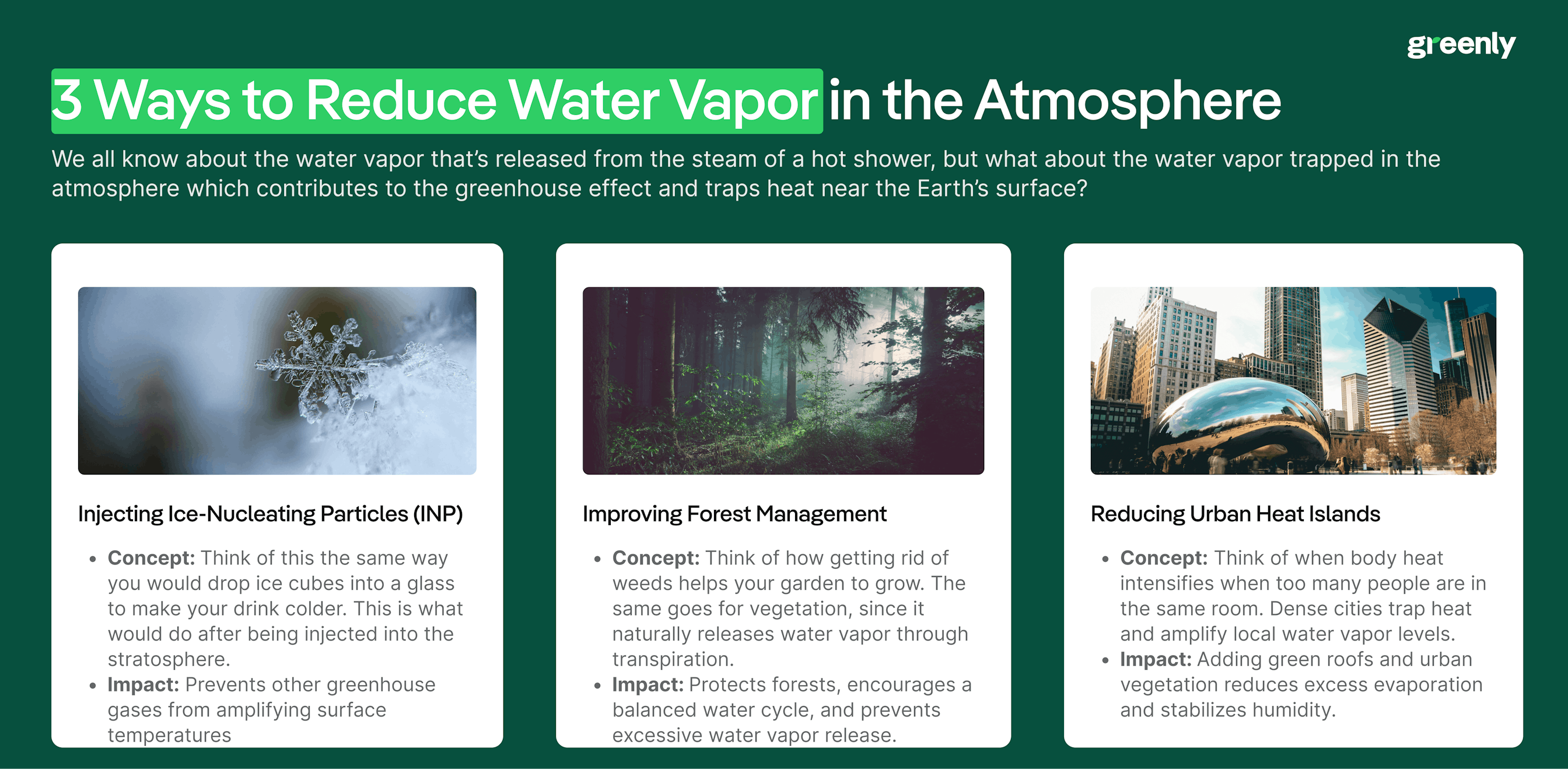
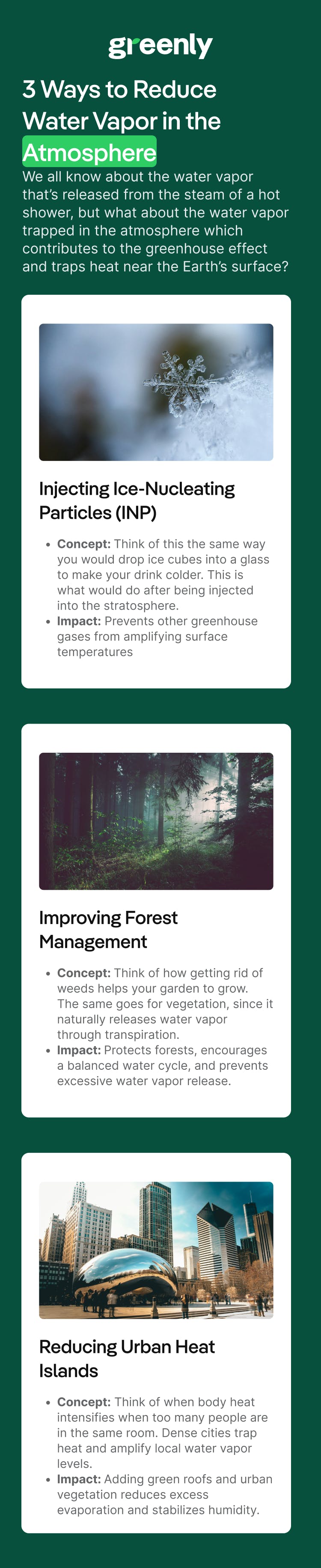
The drop down sections will reveal a few other ways that we could reduce the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere:
Overall, water vapor is indeed a greenhouse gas – but it acts more as an indicator to how many other greenhouse gasses are currently in the atmosphere and exacerbates the greenhouse gas effect.
There are currently several ways to reduce the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere, but the most effective way to prevent water vapor from impacting our planet is to make an effort to reduce all other greenhouse gas emissions along the way.
FAQs on Water Vapor
What About Greenly?
If reading this article about water vapor and greenhouse gasses has made you interested in reducing your carbon emissions to further fight against climate change – Greenly can help you!
It can be overwhelming to figure out how climate policies could have an impact on your business, but don’t worry – Greenly is here to help. Click here to schedule a demo to see how Greenly can help you find ways to ensure your company is complying with all current and future environmental regulations.
Greenly can help you make an environmental change for the better, starting with a carbon footprint assessment to know how much carbon emissions your company produces.